- Trending Now
- Foundational Courses
- Data Science
- Practice Problem
- Machine Learning
- System Design
- DevOps Tutorial

Amazon Interview Questions and Answers
Landing a Software Development Engineer (SDE) position at Amazon is a dream for many aspiring software engineers. Known for its interview process, Amazon evaluates candidates on a variety of technical and behavioral competencies. Preparing effectively for this process is crucial, and understanding the types of questions typically asked can give candidates a significant advantage.
Here, we will explore some of the Top Amazon SDE interview questions, covering technical knowledge.
Most Frequently Asked Interview Questions at Amazon
1. K largest elements from a big file or array .
2. Find a triplet a, b, c such that a 2 = b 2 + c 2 . Variations of this problem include finding a triplet with a sum equal to 0. Find a pair with a given sum. All such questions are efficiently solved using hashing. – Practice here
3. Binary tree traversal questions like left view, right view, top view, bottom view, maximum of a level, minimum of a level, children sum property, diameter, etc.
4. Convert a Binary tree to DLL – Practice here
5. Lowest Common ancestor in a Binary Search Tree and Binary Tree.
6. Implement a stack with push(), pop() and min() in O(1) time.
7. Reverse a linked list in groups of size k – Practice here
8. Given two numbers represented by two linked lists, write a function that returns sum list – Practice here
9. Rotate a matrix by 90 degree.
10. Stock span problem
11. Next greater element
12. Some Dynamic Programming problems like:
- Maximum sum subarray such that no elements are consecutive – Practice here
- Edit distance
- Assembly line scheduling
13. Why Amazon?
14. Questions about projects done in previous company or final year.
15. Important Links :
- Amazon Interview Experiences
- Amazon Practice Questions
- Amazon’s most frequently asked Questions – Set 2
- Amazon Recruitment Process
Amazon Interview Video.
Amazon SDE Interview Questions – FAQs
What are the most common types of technical questions asked in an amazon sde interview.
Amazon SDE interviews commonly feature questions on data structures, algorithms, coding problems, and system design. These assess a candidate’s problem-solving skills and technical knowledge.
How important are Amazon’s leadership principles in the interview process?
Amazon’s leadership principles are crucial. Behavioral questions are designed to evaluate a candidate’s alignment with these principles, ensuring they fit well within the company culture.
What is the STAR method, and how should I use it in my Amazon SDE interview?
The STAR method (Situation, Task, Action, Result) is a structured way to answer behavioral questions, helping you provide clear and concise responses that highlight your past experiences effectively.
4. How can I prepare for system design questions in an Amazon SDE interview?
To prepare for system design questions, study scalable system architecture concepts, practice designing complex systems, and review common design patterns and trade-offs.
Similar Reads
- Amazon Interview Questions and Answers Landing a Software Development Engineer (SDE) position at Amazon is a dream for many aspiring software engineers. Known for its interview process, Amazon evaluates candidates on a variety of technical and behavioral competencies. Preparing effectively for this process is crucial, and understanding t 3 min read
- Amazon SDE Sheet: Interview Questions and Answers 2024 Amazon SDE sheet is the collection of the most important topics or the most frequently asked question in Amazon Software Development Engineer Interviews. Here we have collected all the interview questions and answers to land a job on Amazon table{ display: inline-table !important; width: 100% !impor 11 min read
- AWS Interview Questions Amazon Web Services (AWS) stands as the leading cloud service provider globally, offering a wide array of cloud computing services. It's the preferred choice for top companies like Netflix, Airbnb, Spotify, and many more due to its scalability, reliability, and extensive feature set. AWS was started 15+ min read
- Amazon Interview Questions | Set 146 I am happy to contribute to a community that helped me learn so much. This mail contains info about a recent interview I had with Amazon. First roundQuestion 1 Problem statement: Given an Amazon reviews paragraph containing several words, find the minimum distance between two given words. Example: F 3 min read
- Amazon Interview Preparation Amazon is quite a popular and leading tech organization, not only because of its product and services but also for providing numerous remarkable career opportunities to tech enthusiasts. But to get worthwhile job opportunities at Amazon such as Amazon SDE or Amazon SDET is not very much easy as you 2 min read
- Amazon Interview | Set 44 (For Internship) The written round was relatively easy. It contained 20 multiple choice questions on basic c, algorithms and finite automata. Some questions from OS and networking were there too but were easy. Coding questions were: Find the nodes of the tree as seen from the left view of the binary tree.Rotate the 2 min read
- Amazon Interview | Set 52 (For Internship) Hi All, Here is my interview experience with Amazon for internship. Hope it helps: Round 1: Online round with 20 objective questions on (Questions related to data structures, analysis of algorithms, C Language and some puzzles.) and 2 coding questions in 90 minutes Write a program to reverse k alter 2 min read
- Amazon telephonic interview questions for SDE 1 Ques1. Find top 10 selling product given the count of sales of each product. Ques2. Design a valet parking lot with basic use-case of assigning ticket to customer and retrieving the car later. Three sizes available. Use best fit and nearest distance. All Practice Problems for Amazon ! 1 min read
- Amazon Interview | Set 45 (For Internship) Hello everyone! Recently I sat for an on-campus internship recruiting process of Amazon. The process consisted of a written round followed by two face to face interviews. Written Round: This round consisted of 20 MCQs and two coding questions. We had to complete the test in 90 minutes. The MCQs main 2 min read
- Amazon’s most frequently asked interview questions | Set 2 Amazon's Most Frequently Asked Questions | Set 1 Level - Easy Get minimum element from the stack - Practice hereSerialize and deserialize a binary tree - Practice herePrint a binary tree in a vertical order - Practice hereCelebrity problem - Practice hereLevel order traversalSwap the kth element fro 2 min read
- Amazon Campus Interviews Amazon campus recruitment process basing on the past selection process. Amazon campus recruitment process #1: In this process, there are 4 rounds. Written Round: The Written round consists of 3 sections, Aptitude, Verbal ability, and Technical. There are 30 Questions in the Aptitude section. The imp 2 min read
- Amazon Interview | Set 43 (On-Campus) Questions asked in Amazon Interview. Round 2: Written 1. Find the SQRT of a number. 2. Simulate Reversed level order traversal. Three F2Fs. F2F 1: 1. Given a binary tree, no two adjacent nodes have same color, but all leaves should be in same color. You can fill only with two colors. Write a functio 2 min read
- Amazon Interview | Set 99 (On-Campus) Amazon interview experience :- 1st Round :- 20 mcq and 2 coding questions 1. Left view of binary tree 2. addition of 3 link list 2nd round F2F :- 1. check listlist is palindrome or not 2. level order traversal in spiral form 3rd round :- 1. Length of the longest substring without repeating character 2 min read
- Amazon Interview | Set 42 (On-Campus) Following questions were asked during interview. 1. Given an array, find the longest increasing subsequence of size 3 with max product, all numbers are positive. 2. Given 3 linked lists representing 3 numbers, add them and return the result as another list (take care that your method handles overflo 2 min read
- Amazon Interview Experience | 2 Months Internship I applied for a two-month internship at Amazon through their website, and part of the process was taking an Online Assessment (OA) within 15 days of applying. The OA consisted of two coding questions and a few behavioral questions. Fortunately, I was able to solve both coding problems and confidentl 2 min read
- Amazon Interview | Set 112 (On-Campus) Amazon visited our campus and was hired as intern. These are the questions that I faced. Online Round (90 minutes) 20 Basic MCQs (Data structure, C, C++, OS, Aptitude, Networks). 2 programs : 1. Given a text txt[0..n-1] and a pattern pat[0..m-1], write a function search(char pat[], char txt[]) that 2 min read
- Amazon Interview Experience | 2 months Internship It was a one-hour technical interview under AmazeWoW program for 2 months internship after the third year. First 20 minutes: The interviewer started with asking questions on OOP concepts, revolving around abstraction, polymorphism, inheritance, accessibility of variables. After OOP, we moved to Comp 1 min read
- Amazon Interview | Set 116 (On-Campus) Round 1:- 20 MCQ’s(Majority from OS and Java, C++, 1 aptitude) 2 coding questions. 1. Given an array, find the maximum sum that can be formed from the array such that no two adjacent elements are taken into consideration. for ex:- 1,2,3,5 should return 7. 2. Print Vertical axis sum of the given bina 2 min read
- Amazon Interview Experience | Set 368 (Phone and Onsite) Phone interview Deep copy of linked list Onsite interview Question on map reduce, find if all words in a file are palindrome Design Elevator with OOPS concept Design Twitter Problem related to amazon Compare two expressions and check if they are similar. for example -(a+b+b) = -a-c-b Related Practic 1 min read
- Interview Preparation
- Interview Questions
- Interview Tips
- interview-questions
- placement preparation
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
Cracking the top Amazon coding interview questions
Landing a job at Amazon is a dream for many developers around the globe. Amazon is one of the largest companies in the world, with a workforce of over half a million strong.
For you to join them, you’ll need to complete their unique interview that combines technical and leadership knowledge.
Today, we’ll walk you through everything you need to crack the Amazon technical interview , including questions and answers for coding problems and a step-by-step tech interview prep guide .
Amazon Leetcode Questions #
Amazon is a dream company for many developers. To get yourself a job at Amazon, the most important part is to practice your interview skills and apply for the correct position. Make sure you thoroughly look at the job description to ensure that it matches your skill set. The next step is to practice some Amazon Leetcode Questions. Solving Leetcode problems is an exceptional way to practice your coding skills.
Educative has curated a collection of Amazon-specific LeetCode problems to facilitate focused practice. There’s no need to feel overwhelmed by the vast array of over 2000+ LeetCode problems. With this select set, you can practice and develop the logic necessary to tackle all the coding problems typically encountered in Amazon interviews. We’veve also added 40+ commonly asked Amazon coding interview questions for you to practice and improve your skills. For detailed lists of questions curated to help you ace the Amazon coding interviews, Educative-99 and Educative-77 are the perfect places to start.
Answer any Amazon interview question by learning the patterns behind common questions. # Grokking Coding Interview Patterns in Python Grokking Coding Interview Patterns in JavaScript Grokking Coding Interview Patterns in Java Grokking Coding Interview Patterns in Go Grokking Coding Interview Patterns in C++
45 common Amazon technical coding interview questions #
1. find the missing number in the array #.
You are given an array of positive numbers from 1 to n , such that all numbers from 1 to n are present except one number x . You have to find x . The input array is not sorted. Look at the below array and give it a try before checking the solution.
View the find the missing number solution in C++, Java, JavaScript, and Ruby.
A naive solution is to simply search for every integer between 1 and n in the input array, stopping the search as soon as there is a missing number. However we can do better. Here is a linear, O ( n ) O(n) O ( n ) , solution that uses the arithmetic series sum formula. Follow the steps below to find the missing number:
Find the sum sum_of_elements of all the numbers in the array.
Then, find the sum actual_sum of the first n numbers using the arithmetic series sum formula n ( n + 1 ) / 2 n(n+1)/2 n ( n + 1 ) /2 .
The difference between these, i.e., actual_sum - sum_of_elements , is the missing number in the array.
Runtime complexity: Linear, 𝑂 ( 𝑛 ) 𝑂(𝑛) O ( n )
Memory complexity: Constant, 𝑂 ( 1 ) 𝑂(1) O ( 1 )
2. Determine if the sum of two integers is equal to the given value #
Given an array of integers and a value, determine if there are any two integers in the array whose sum is equal to the given value. Return true if the sum exists and return false if it does not. Consider this array and the target sums:
View the sum of two integers solution in C++, Java, JavaScript, and Ruby.
We can use the following algorithm to find a pair that adds up to target .
Scan the whole array once and store visited elements in a hash set.
During the scan, for every element num in the array, we check if target - num is present in the hash set, i.e., target - num is already visited.
If target - num is found in the hash set, it means there is a pair ( num , target - num ) in the array whose sum is equal to the given target , so we return TRUE.
If we have exhausted all elements in the array and found no such pair, the function will return FALSE.
Runtime complexity: Linear, O ( n ) O(n) O ( n )
Memory complexity: Linear, O ( n ) O(n) O ( n )
3. Merge two sorted linked lists #
Given two sorted linked lists, merge them so that the resulting linked list is also sorted. Consider two sorted linked lists and the merged list below them as an example.
View the merge two sorted linked lists solution in C++, Java, JavaScript, and Ruby.
Given that head1 and head2 are pointing to the head nodes of the given linked lists, respectively, if one of them is None , return the other as the merged list. Otherwise, perform the following steps:
Compare the data of the first nodes of both lists and initialize the merged_head to the smaller of the two nodes. Also, initialize merged_tail as merged_head . Move the smaller node pointer ( head1 or head2 ) to the next node.
Perform the following steps until either head1 or head2 is NULL:
Compare the data of the current nodes pointed by head1 and head2 , append the smaller node to merged_tail , and move the corresponding pointer forward.
Update merged_tail to the appended node.
After exiting the loop, if either list has remaining nodes, append the remaining nodes to the end of the merged list. Do this by updating the next pointer of merged_tail to point to the remaining nodes.
Return merged_head , which represents the head of the merged list.
Runtime complexity: Linear, 𝑂 ( 𝑚 + 𝑛 ) 𝑂(𝑚+𝑛) O ( m + n ) , where m m m and n n n are lengths of both linked lists.
4. Copy linked list with arbitrary pointer #
You are given a linked list where the node has two pointers. The first is the regular next pointer. The second pointer is called arbitrary and it can point to any node in the linked list. Your job is to write code to make a deep copy of the given linked list. Here, deep copy means that any operations on the original list should not affect the copied list.
View the copy linked list solution in C++, Java, JavaScript, and Ruby.
If the given linked list’s head is NULL, return NULL as the copied list.
Initialize a current pointer with head to traverse the original linked list. Also, initialize new_head and new_prev pointers to NULL to keep track of the copied list. Additionally, create an empty dictionary (hashmap) named ht to map nodes in the original and copied lists.
Traverse the original linked list while creating a copy of each node. For each node:
Create a new_node with the same data as the current node.
Copy the arbitrary pointer of the current node to the new_node . Therefore, for now, we are pointing the arbitrary pointer of the new_node to where it is pointing in the original node.
If new_node is the first node in the copied list, set new_head and new_prev to new_node . Otherwise, connect the new_node to the copied list by setting new_prev.next to new_node and set new_prev to new_node .
Store copied node new_node in the ht with the key current . This will help us point the arbitrary pointer of the copied nodes to the correct new nodes in the copied list.
For now, the arbitrary pointers in the new nodes point to nodes in the original list. To update them, we traverse the new list using new_current , utilize the hashmap ht to find the corresponding copied node for each original node pointed to by the arbitrary pointer, and then update the arbitrary pointer of the current node to point to this copied node.
Once all arbitrary pointers are updated, return new_head , which represents the head of the copied list.
5. Level order traversal of binary tree #
Given the root of a binary tree, display the node values at each level. Node values for all levels should be displayed on separate lines. Let’s take a look at the below binary tree.
View the level order traversal of binary tree solution in C++, Java, JavaScript, and Ruby.
Initialize a queue, queue , with the root node.
Iterate over the queue until it’s empty:
For each level, calculate the size ( level_size ) of the queue.
Initialize an empty list level_nodes .
Iterate level_size times:
Dequeue a node from the queue .
Append the value of the dequeued node in level_nodes .
Enqueue the left child and the right child of the dequeued node in queue , if they exist.
Convert level_nodes to a comma-separated string and store it in result .
Return the result .
6. Determine if a binary tree is a binary search tree #
Given a Binary Tree, figure out whether it’s a Binary Search Tree . In a binary search tree, each node’s key value is smaller than the key value of all nodes in the right subtree, and is greater than the key values of all nodes in the left subtree. Below is an example of a binary tree that is a valid BST.
Below is an example of a binary tree that is not a BST.
View the binary tree solution in C++, Java, JavaScript, and Ruby.
We use a recursive method to explore the binary tree while keeping track of the allowed range for each node’s value. At the start, the root node’s value can be any number. As we go down the tree, we adjust this range. For a left child, the value must be smaller than its parent’s value. For a right child, the value must be larger than its parent’s value. By doing this, we make sure that each node’s value is within the acceptable range set by its parent. If we find any node with a value outside this range, it means the tree doesn’t follow the rules of a binary search tree and is not valid as a BST.
Define a recursive function is_bst_rec that takes a node, min_val , and max_val as parameters.
Inside the function:
Check if the node is NULL. If so, return TRUE.
Verify if the current node’s value node.val lies within the acceptable range defined by min_val (exclusive) and max_val (exclusive). If not, return FALSE.
Recursively call is_valid for the left subtree with the updated max_val as the current node’s value and for the right subtree with the updated min_val as the current node’s value.
Initialize the range by calling is_bst_rec with the root node, setting min_val to negative infinity and max_val to positive infinity.
7. String segmentation #
You are given a dictionary of words and a large input string. You have to find out whether the input string can be completely segmented into the words of a given dictionary. The following two examples elaborate on the problem further.
Given a dictionary of words.
Input string of “applepie” can be segmented into dictionary words.
Input string “applepeer” cannot be segmented into dictionary words.
View the string segmentation solution in C++, Java, JavaScript, and Ruby.
The algorithm iteratively checks substrings of the input string against the dictionary. Starting with an empty string being segmentable, it gradually builds up segmentability information for larger substrings by considering all possible substrings and checking if they exist in the dictionary. Once we determine that a substring can be segmented into words from the dictionary, we mark the corresponding entry in an array dp array as TRUE. Subsequently, when processing longer substrings, we use dp to check whether shorter substrings within them have already been determined to be segmentable, avoiding recomputations.
Initialize a variable n with the length of the input word and create a boolean array dp with a size of n + 1 . Initialize all values of dp to FALSE.
Set dp[0] to TRUE to indicate that the empty string can be segmented.
Iterate over the indexes of the word from 1 to n .
For each index i , iterate over the indexes j from 0 to i - 1 .
Check if dp[j] is TRUE and if the substring word[j:i] exists in the dictionary.
If both conditions are met, set dp[i] to TRUE.
After completing the iterations, return dp[n] to indicate whether the entire word can be segmented.
Runtime complexity: Polynomial, O ( n 3 ) O(n^3) O ( n 3 )
8. Reverse words in a sentence #
Reverse the order of words in a given sentence (a string of words).
View the reverse words in a sentence solution in C++, Java, JavaScript, and Ruby.
The essence of this algorithm is to reverse the words in a string by a two-step method using two pointers, effectively manipulating the string in place. Initially, the entire string is reversed, which correctly repositions the words in reverse order. However, due to this reversal of the string, the corresponding characters of words are also reversed. To correct the order of the characters, iterate through the string, and identify the start and end of each word, considering space as a delimiter between words. Set two pointers at the start and end of the word to reverse the characters within that word. By repeating this process for each word, the method effectively achieves the goal without requiring additional memory.
Convert the string, sentence , into a list of characters and store it back in sentence .
Get the length of the sentence and store it in str_len .
Define a str_rev function to reverse the entire list of characters sentence .
Set the start pointer start to 0 and iterate over the range from 0 to str_len + 1 using the pointer end .
When encountering a space or reaching the end of a word, reverse the characters of the word using the str_rev function with sentence , start , and end - 1 as arguments.
Update the start pointer start to end + 1 .
Join the list of characters back into a string using join(sentence) .
Return the reversed string.
Memory complexity: Constant, O ( 1 ) O(1) O ( 1 )
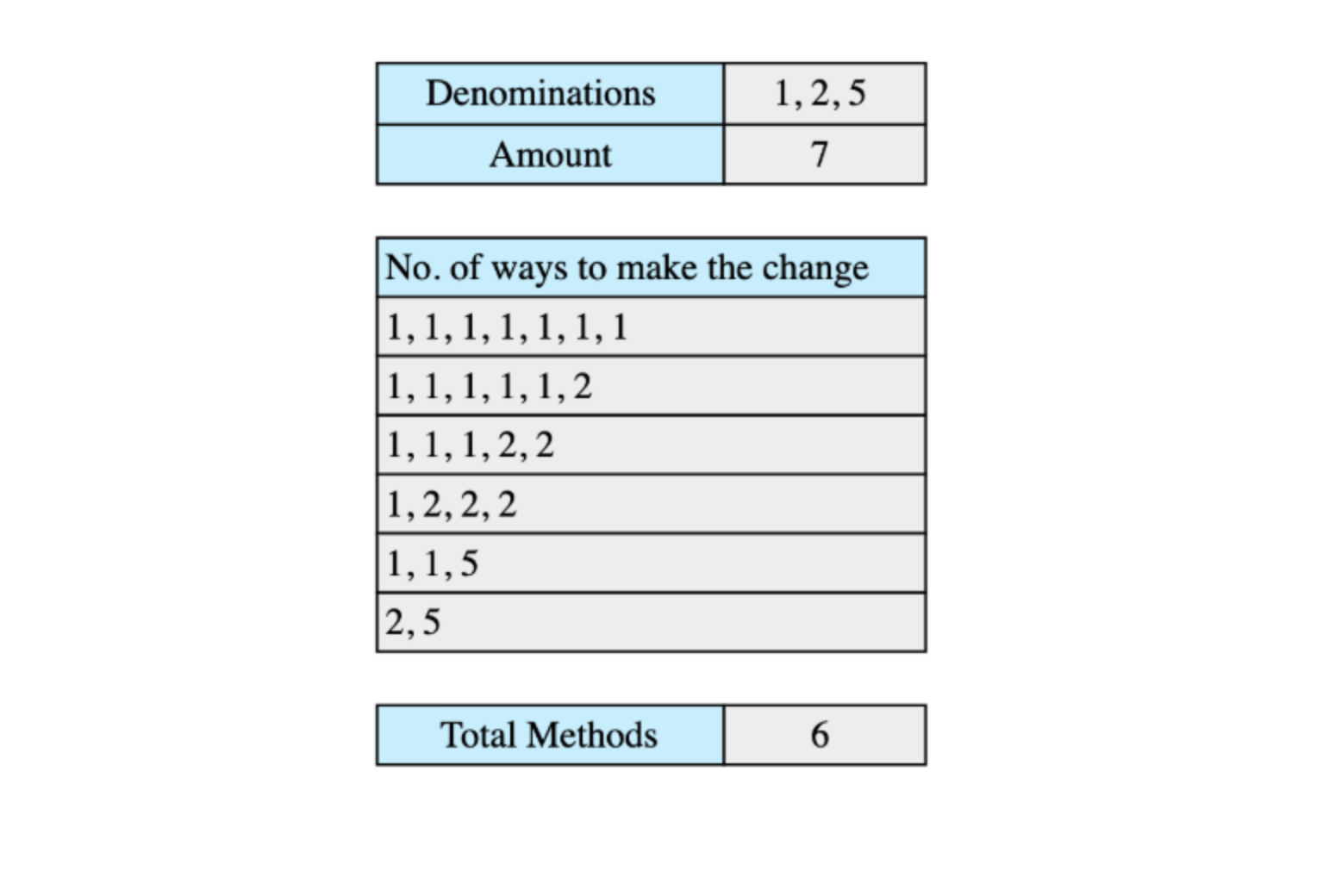
9. How many ways can you make change with coins and a total amount #
Suppose we have coin denominations of [1, 2, 5] and the total amount is 7. We can make changes in the following 6 ways:
View the coin changing problem solution in C++, Java, JavaScript, and Ruby.
We can use dynamic programming to build simple coin change solutions, store them, and utilize them in larger coin change amounts. We start by considering the simplest case, which is making change for an amount of zero. At this stage, there’s only one way to make a change, which is by using no coins. Then, we proceed to compute the number of ways to make change for larger amounts by considering each coin denomination one by one. For each denomination, we iterate through the possible amounts starting from the denomination value up to the target amount. At each step, we update the count of ways to make change for the current amount by incorporating the count for smaller amounts. This iterative process ensures that we exhaustively explore all valid combinations of coins, leading to an accurate count of the total number of ways to make change for the target amount.
Initialize an array dp of size (amount + 1) to track the number of ways to make change.
Set dp[0] = 1 to denote the one way to make change for an amount of zero.
Iterate through each coin denomination:
For each denomination den , iterate from den to amount .
Update dp[i] by adding dp[i - den] to account for the current denomination.
After processing all denominations and amounts, dp[amount] holds the total number of ways to make change.
Runtime complexity: Quadratic, 𝑂 ( 𝑚 ∗ 𝑛 ) 𝑂(𝑚∗𝑛) O ( m ∗ n )
Memory complexity: Linear, 𝑂 ( 𝑛 ) 𝑂(𝑛) O ( n )
10. Find Kth permutation #
Given a set of ‘n’ elements, find their Kth permutation. Consider the following set of elements:
All permutations of the above elements are (with ordering):
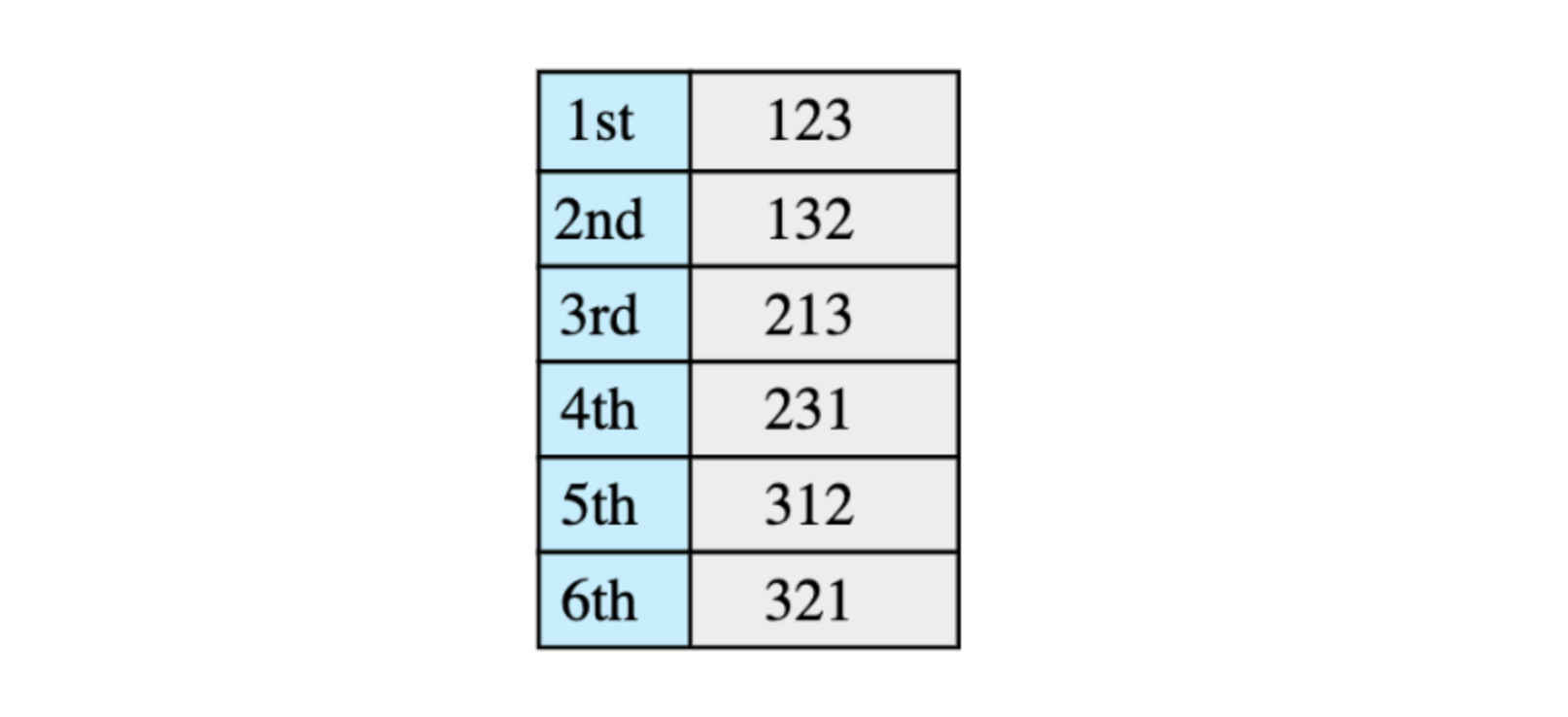
Here we need to find the Kth permutation.
View the find Kth permutation solution in C++, Java, JavaScript, and Ruby.
We can divide all possible permutations into blocks, where each block represents a group of permutations sharing the same first element, and determine which block the target permutation belongs to by dividing the target position by the number of permutations within each block (block size).
Next, we can determine the first element of the permutation, based on the block’s position within all permutations and add it to our result. We also remove the selected element from the original set of elements to prevent duplication in the permutation.
Now, we can repeat the same process to find the remaining elements of the required permutation using the now reduced set of elements. We skipped the b l o c k _ s i z e ∗ # o f b l o c k s block\_size * \# of blocks b l oc k _ s i ze ∗ # o f b l oc k s we passed over. This tells us how many permutations we’ve missed. So, within the chosen block, we’re now looking for the ( k − s k i p p e d p e r m u t a t i o n s ) t h (k - skipped permutations)th ( k − s ki pp e d p er m u t a t i o n s ) t h permutation. We can adjust k this way and repeat the same process on the updated, smaller block of numbers.
To implement the algorithm:
Start by defining a function called find_kth_permutation . This takes three parameters: v (the input list), k (the target position), and result (the result string).
Check if v is empty. If so, return.
Calculate the number of permutations starting with the first digit of v and store it in count . This is done by computing the factorial of (n - 1) using the function factorial , where n is the length of v .
Determine the target block by dividing k-1 by the number of blocks count and save in selected .
Add the selected element v[selected] to result , and remove it from v .
Update k to reflect the remaining permutations by subtracting count multiplied by selected from k .
Recursively call the function with the updated parameters until v is empty or k is 0.
Runtime complexity: Quadratic, 𝑂 ( 𝑛 2 ) 𝑂(𝑛^2) O ( n 2 )
11. Find all subsets of a given set of integers #
We are given a set of integers and we have to find all the possible subsets of this set of integers. The following example elaborates on this further.
Given set of integers:
All possile subsets for the given set of integers:
View the find all subsets solution in C++, Java, JavaScript, and Ruby.
Instead of using nested loops to generate all possible combinations, this algorithm employs binary representation to efficiently derive all subsets of a given set. There are 2 n 2^n 2 n subsets, where n n n represents the size of the original set. The algorithm decodes the binary representation of each number, ranging from 0 0 0 to 2 n − 1 2^n-1 2 n − 1 , determining which elements to include or exclude in the subsets. It makes this decision by examining each bit of the binary representation, where a 1 indicates inclusion and a 0 indicates exclusion of the corresponding element.
Calculate the total number of subsets subsets_count , which is 2 n 2^n 2 n .
Iterate through numbers from 0 to subsets_count - 1 using a for loop.
Inside the loop, create an empty set called st to store the current subset.
Iterate through each index j of the input list nums using another for loop.
Write and use the function get_bit to determine whether the jth bit of the current number i is set to 1 or 0 .
If the jth bit of i is 1 , add the corresponding element from nums to the current subset st .
After iterating through all indexes of nums , append the current subset st to the list sets .
Runtime complexity: Exponential, 𝑂 ( 2 𝑛 ∗ 𝑛 ) 𝑂(2^𝑛∗𝑛) O ( 2 n ∗ n )
Memory complexity: Exponential, 𝑂 ( 2 𝑛 ∗ 𝑛 ) 𝑂(2^𝑛∗𝑛) O ( 2 n ∗ n )
12. Print balanced brace combinations #
Print all braces combinations for a given value n so that they are balanced. For this solution, we will be using recursion.
View the print balanced brace combinations solution in C++, Java, JavaScript, and Ruby.
The algorithm has the following main points:
Adding parentheses :
Determine whether to add a left parenthesis “{” or a right parenthesis “}” based on certain conditions:
If the count of left parentheses ( left_count ) is less than n , a left parenthesis can be added to make a valid combination.
If the count of right parentheses ( right_count ) is less than the count of left parentheses ( left_count ), a right parenthesis can be added to make a valid combination.
Constructing the result: As the algorithm explores different combinations of parentheses, when left_count and right_count both reach n , indicating that n pairs of parentheses have been added and the combination is complete, it appends the current combination present in the output list to the result list.
Backtracking :
After exploring a possible path by adding a parenthesis and making recursive calls, the algorithm backtracks to explore other possible combinations.
Backtracking involves removing the last added parenthesis from the output list using the pop operation.
This reverts the output list to its state before the current recursive call, allowing the algorithm to explore other possible combinations without missing any.
Initialize an empty list output to store the current combination and an empty list result to store all valid combinations.
Define a print_all_braces_rec function with parameters n (the total number of pairs), left_count , right_count , output , and result .
Inside print_all_braces_rec :
Check if both left_count and right_count are greater than or equal to n . If TRUE, append a copy of output to result .
If left_count is less than n , add a left parenthesis { to output , and recursively call print_all_braces_rec with n , left_count + 1 , right_count , output , and result .
After the recursive call, remove ( pop ) the last element from output to backtrack.
If right_count is less than left_count , add a right parenthesis } to output , and recursively call print_all_braces_rec with n , left_count , right_count + 1 , output , and result .
Return the result list containing all valid combinations of well-formed parentheses pairs for the given n .
Runtime complexity: Exponential, O ( 2 n ) O(2^n) O ( 2 n )
13. Clone a directed graph #
Given the root node of a directed graph, clone this graph by creating its deep copy so that the cloned graph has the same vertices and edges as the original graph.
Let’s look at the below graphs as an example. If the input graph is G = ( V , E ) G = (V, E) G = ( V , E ) where V is set of vertices and E is set of edges, then the output graph (cloned graph) G’ = (V’, E’) such that V = V’ and E = E’. We are assuming that all vertices are reachable from the root vertex, i.e. we have a connected graph.
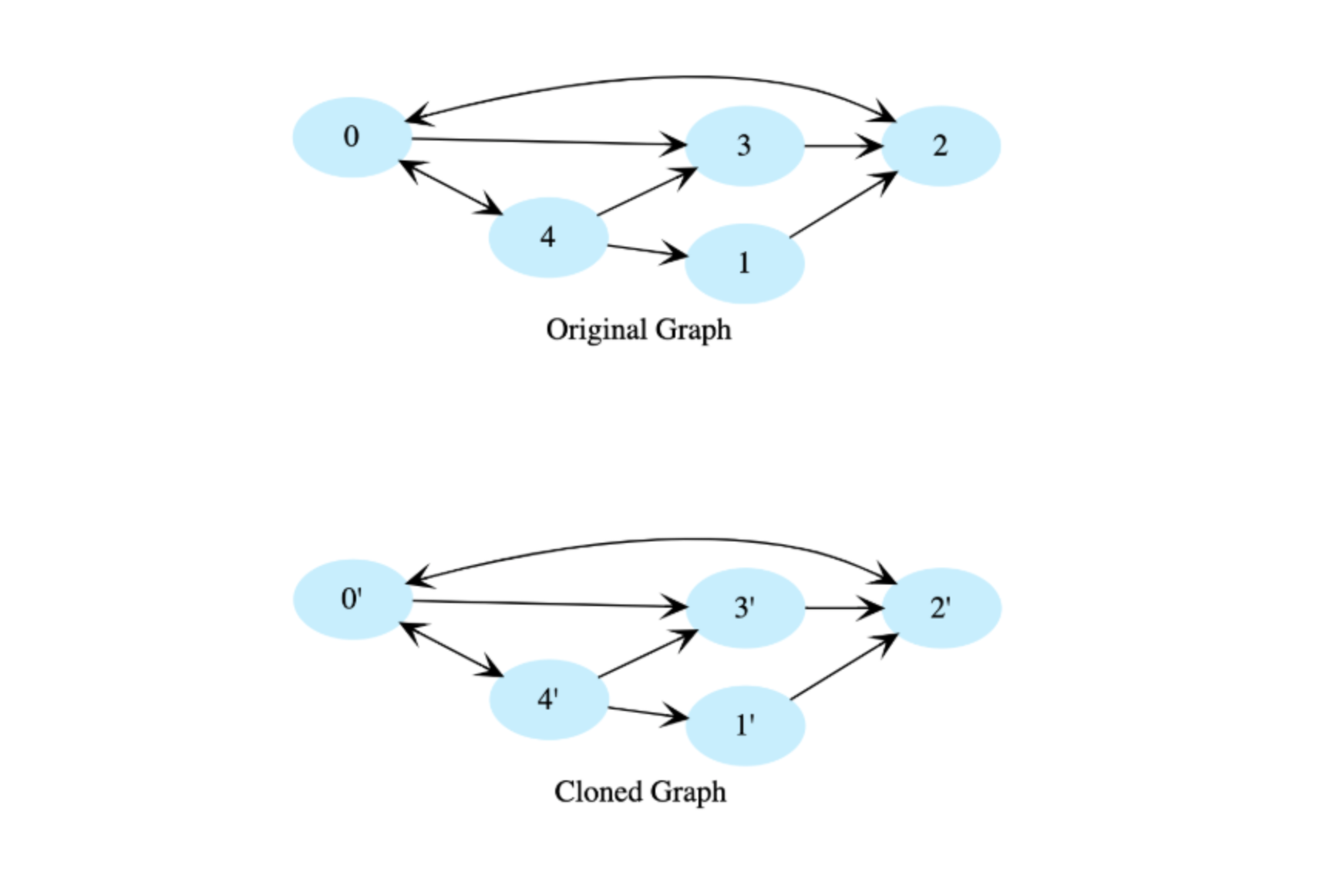
View the clone a directed graph solution in C++, Java, JavaScript, and Ruby.
This algorithm clones a directed graph by traversing it recursively. It creates a new node for each encountered node, replicates its data, and traverses its neighbors. If a neighbor has already been cloned, it uses the existing clone; otherwise, it recursively clones the neighbor. This process continues until all nodes and their relationships are replicated, resulting in a deep copy of the original graph.
Initialize an empty dictionary called nodes_completed to keep track of cloned nodes.
Write clone_rec function, which takes root node of the original graph and the nodes_completed dictionary as parameters. Inside the function:
If the root node is None, return None.
Otherwise, create a new node p_new with the same data as the root and add it to the nodes_completed dictionary to mark it as visited.
Iterate through each neighbor p of the root node:
If the neighbor p has not been cloned yet (i.e., not present in nodes_completed ), recursively call clone_rec with p and nodes_completed , and add the clone to the neighbors list of p_new .
If the neighbor p has already been cloned, retrieve the clone x from nodes_completed and add it to the neighbors list of p_new .
Call clone_rec and pass root and nodes_completed as parameters. When its recursion completes, return the cloned graph rooted at p_new .
14. Find low/high index #
Given a sorted array of integers, return the low and high index of the given key. You must return -1 if the indexes are not found. The array length can be in the millions with many duplicates.
In the following example, according to the key , the low and high indices would be:
- key : 1, low = 0 and high = 0
- key : 2, low = 1 and high = 1
- ke y: 5, low = 2 and high = 9
- key : 20, low = 10 and high = 10
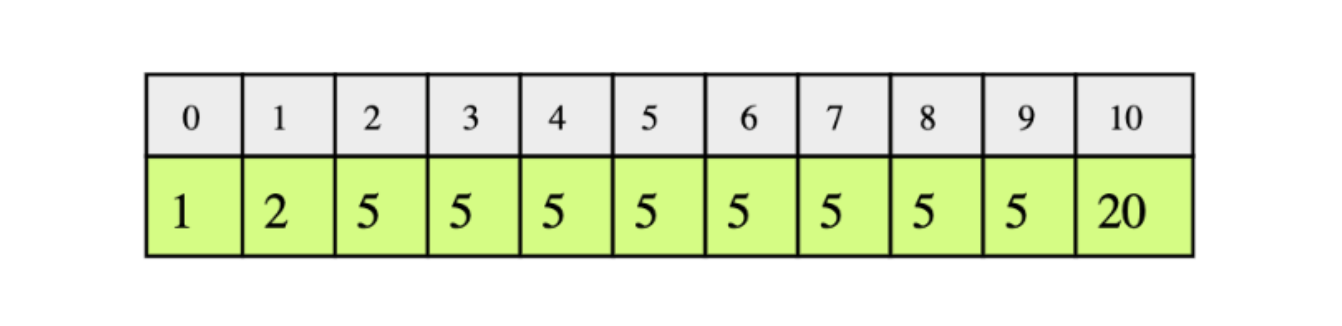
For the testing of your code, the input array will be:
View the find low/high index solution in C++, Java, JavaScript, and Ruby.
We can modify the binary search algorithm to find the first occurrence of the key by narrowing down the search range even if the value at the mid is equal to the key. The algorithm is designed to always move to the left whenever it encounters an element that’s equal to or greater than the target. So, when the search range is narrowed down to a single element, and that element matches the target, it means that this is the leftmost occurrence of the target element in the array. Similarly, to find the last occurrence of a key, we adjust the search range toward the right whenever the middle element is less than or equal to the key. This iterative process continues until the search range narrows down to a single element. At this point, either the last occurrence of the key is found, or it confirms the absence of the key in the array. To implement the algorithm:
Initialize low to 0, high to the length of the array minus one, and mid to high / 2 .
Enter a while loop that continues while low is less than or equal to high .
Inside the loop, set mid_elem to arr[mid]
Compare mid_elem with the key:
If mid_elem is less than the key, update low to mid + 1 .
Otherwise, update high to mid - 1 .
Update mid to low + (high - low) / 2 .
After the loop, check if low is within the bounds of the array and if the element at index low equals the key. If so, return low . Otherwise, return -1 .
Repeat the same steps to find the last occurrence, with the only difference being in the comparison step. If mid_elem is less than or equal to the key, update low to mid + 1 ; and if it’s greater than the key, update high to mid - 1 .
Runtime complexity: Logarithmic, O ( l o g n ) O(logn) O ( l o g n )
15. Search rotated array #
Search for a given number in a sorted array, with unique elements, that has been rotated by some arbitrary number. Return -1 if the number does not exist. Assume that the array does not contain duplicates.

View the search rotated array solution in C++, Java, JavaScript, and Ruby.
To tackle rotation in a binary search for a rotated array, we adjust the search range based on the middle element’s comparisons as follows:
If the element at the middle index matches the target, return the index of the middle element, as the target has been found.
If the element at the middle index is greater than or equal to the element at the start index, it implies that the left subarray (from the start to the middle) is sorted:
Now, check if the target falls within the range of elements from the leftmost element to the middle element. If it does, adjust the search range to focus on the left subarray.
Otherwise, adjust the search range to focus on the right subarray.
If the element at the middle index is less than the element at the end index, it indicates that the right subarray (from the middle to the end) is sorted:
Check if the target falls within the range of elements from the middle element to the rightmost element. If it does, adjust the search range to focus on the right subarray.
Otherwise, adjust the search range to focus on the left subarray.
Initialize low to 0 and high to the length of the array minus one.
Inside the loop, calculate mid using the formula low + (high - low) // 2 .
Check if the element at the middle index matches the target. If it does, return the index of the middle element.
If arr[low] is less than or equal to arr[mid] , it implies that the left subarray (from low to mid) is sorted:
If the target falls within this range, update the high to mid - 1 . Otherwise, update the low to mid + 1 .
Otherwise, it’s obvious that arr[low] is greater than arr[mid] , which it indicates that the right subarray (from mid to high) is sorted:
If the target falls within this range, update the low to mid + 1 . Otherwise, update the high to mid - 1 .
If the target is not found after the loop, return -1 to indicate its absence in the array.
More common Amazon technical coding interview questions #
- K largest elements from an array
- Convert a Binary tree to DLL
- Given a binary tree T , find the maximum path sum. The path may start and end at any node in the tree.
- Rotate a matrix by 90 degrees
- Assembly line scheduling with dynamic programming
- Implement a stack with push() , min() , and pop() in O ( 1 ) O(1) O ( 1 ) time
- How do you rotate an array by K?
- Design Snake Game using Object Oriented Programming analysis and design technique.
- Print all permutations of a given string using recursion
- Implement a queue using a linked list
- Find the longest increasing subsequence of an array
- Lowest common ancestor in a Binary Search Tree and Binary Tree
- Rotate a given list to the right by k places, which is non-negative.
- Write a function that counts the total of set bits in a 32-bit integer.
- How do you detect a loop in a singly linked list?
- Reverse an array in groups
- Given a binary tree, check if it’s a mirror of itself
- Josephus problem for recursion
- Zero Sum Subarrays
- Huffman Decoding for greedy algorithms
- Egg Dropping Puzzle for dynamic programming
- N-Queen Problem
- Check if strings are rotations of each other
- 0-1 Knapsack Problem
- Unbounded knapsack problem
- Longest palindromic subsequence
- Print nth number in the Fibonacci series
- Longest common substring
- Longest common subsequence

Overview of the Amazon technical coding interview #
To land a software engineering job at Amazon, you need to know what lies ahead. The more prepared you are, the more confident you will be. So, let’s break it down.
Interview Timeline: The whole interview process takes 6 to 8 weeks to complete.
Types of Interviews: Amazon coding interviews consist of 5 to 7 interviews. This includes 1 assessment for fit and aptitude, 1-2 online tests, and 4-6 on-site interviews, also known as The Loop.
The Loop: The onsite interviews include 1 to 3 interviews with hiring managers and 1 bar raiser interview to evaluate Amazon’s 14 leadership principles.
Coding Questions: Amazon programming questions focus on algorithms, data structures, puzzles, and more.
Hiring Levels: Amazon usually hires at entry-level 4 (out of 12 total), and the average salary for that level ranges from $106,000 to $114,000 yearly.
Hiring Teams: Amazon hires based on teams. The most common hiring teams are Alexa and AWS.
Programming Languages: Amazon prefers the following programming languages for coding questions: Java, C++, Python, Ruby, and Perl.

Amazon’s 14 leadership principles #
Though coding interviews at Amazon are similar to other big tech companies, there are a few differences in their process, in particular, the Bar Raiser . Amazon brings in an objective third-party interviewer called a Bar Raiser, who evaluates candidates on Amazon’s 14 Leadership Principles. The Bar Raiser has complete veto power over whether or not you will be hired.
It is unlikely that you will know which of your interviewers is the Bar Raiser. The key is to take every part of the interview seriously and always assume you’re being evaluated for cultural fit as well as technical competency.
Below are the 14 values that you will be evaluated on.

How to prepare for an Amazon coding interview #
Now that you have a sense of what to expect from an interview and know what kinds of questions to expect, let’s learn some preparation strategies based on Amazon’s unique interview process.
Updating your resume #
Make sure you’ve updated your resume and LinkedIn profile. Always use deliverables and metrics when you can as they are concrete examples of what you’ve accomplished. Typically recruiters will browse LinkedIn for candidates.
If an Amazon recruiter believes that you are a good match they will reach out to you (via email or LinkedIn) to set up a time to chat. Even if you don’t land the job this time, chatting with them is a great chance to network
Prepare for coding assessment #
It’s up to you to come to a coding interview fully prepared for technical assessment. I recommend at least three months of self-study to be successful. This includes choosing a programming language, reviewing the basics, and studying algorithms, data structures, system design , object-oriented programming, OS, and concurrency concepts.
You’ll also want to prepare for behavioral interviews .
It’s best to create a roadmap for your coding interview to keep yourself on track.
Prescreen with a recruiter #
Expect a light 15-30 minute call where the recruiter will gauge your interest level and determine if you’re a good fit. The recruiter may touch on a few technical aspects. They just want to get an idea of your skills. Typical questions might include your past work experiences, your knowledge of the company/position, salary, and other logistical questions.
It’s important to have around 7-10 of your own questions ready to ask the interviewer. Asking questions at an early stage shows investment and interest in the role.
Online Coding Assessment #
Once you complete the call with the recruiter, they’ll administer an online coding test, a debugging test, and an aptitude test. The debugging section will have around 6-7 questions, which you have 30 minutes to solve. The aptitude section will have around 14 multiple-choice questions, dealing with concepts like basic permutation combination and probabilities.
The coding test consists of two questions. You’ll have about 1.5 hours to complete it. Expect the test to be conducted through Codility, HackerRank, or another site. Expect some easy to medium questions that are typically algorithm related. Examples include:
- Reverse the second half of a linked list
- Find all anagrams in a string
- Merge overlapping intervals
Tips to crack Amazon online coding assessment: #
Here are a few easily implemented tips to make the Amazon coding assessment more manageable for yourself:
Use your own preferred editor
- It is best to take the assessment in a familiar environment.
Read each prompt multiple times through
- Sometimes, they may try and trick you with the wording. Make sure that you’re meeting all of the stated requirements before diving in.
Practice with less time than you’re given in the actual assessment
- Time-sensitive tests can be stressful for many people. Help to relieve some of this stress by learning to work faster and more efficiently than you need to be.
Phone Interviews #
Once you’ve made it past the prescreen and online assessment, the recruiter will schedule your video/phone interviews , likely with a hiring manager or a manager from the team you’re looking to join. At this stage in the process, there will be one to three more interviews.
This is where they’ll ask you questions directly related to your resume, as well as data structures, algorithms, and other various coding questions that apply to the position. You can expect to write code, review code, and demonstrate your technical knowledge.
On-Site Interviews: The Loop #
If you have successfully made it through the series of phone interviews, you’ll be invited for an on-site visit. This full day of on-site interviews is referred to as the “The Loop”. Throughout the day, you’ll meet with 4-6 people. Expect half of these interviews to be technical and the other half to assess soft skills. Be prepared to work through questions on a whiteboard and discuss your thought process.
Concepts that Amazon loves to test on are data structures algorithms . It’s important to know the runtimes, theoretical limitations, and basic implementation strategies of different classes of algorithms.
Data structures you should know: Arrays, Stacks, Queues, Linked lists, Trees, Graphs, Hash tables
Algorithms you should know: Breadth First Search, Depth First Search, Binary Search, Quicksort, Mergesort, Dynamic programming, Divide and Conquer
The Offer / No Offer #
Generally, you’ll hear back from a recruiter within a week after your interviews. If you didn’t get an offer, Amazon will give you a call. You’ll likely have to wait another six months to re-apply. Judging that your on-site interviews went well, they’ll reach out to you, at which point they’ll make you an offer, send you documents to sign, and discuss any further questions you have.

Amazon Software Engineer Interview #
Amazon is one of the top tech companies worldwide, and the company focuses on hiring only the best talent. Securing a software engineer position at Amazon is not a piece of cake, but with the right guidance, content, and practice questions, you can ace the Amazon software engineer interview.
Amazon software engineer interviews consist of four rounds. A major part of these four interview rounds involves technical interview questions. That is why having a solid grasp of computing fundamentals is crucial. Questions related to arrays, linked lists, strings, dynamic programming, and system design are common. We have mentioned some of the commonly asked questions above, so have a look and practice them thoroughly. For more interview prep questions, you can try Educative-99 , created to help software engineers secure a job at top tech companies.
Besides technical questions, Amazon software engineer interviews also include behavioral questions. Amazon ensures that candidates are the right fit for the company culture, which is why you’ll be asked several behavioral questions as well. The cornerstone of Amazon’s culture is its 14 Leadership Principles. These principles, which include notions like “Customer Obsession,” “Ownership,” and “Bias for Action,” guide every decision the company makes, from high-level strategies to everyday interactions.
This dual approach to assessing candidates ensures that Amazon software engineers can solve complex technical challenges, collaborate effectively, handle difficult situations, and adapt to the company’s fast-paced environment. Hence, candidates must prepare themselves for both technical and behavioral challenges.
Wrapping up and resources #
Cracking the Amazon coding interview comes down to the time you spend preparing, such as practicing coding questions, studying behavioral interview questions, and understanding Amazon’s company culture. There is no golden ticket , but more preparation will surely make you a more confident and desirable candidate.
To help you prepare for interviews, Educative has created several unique language-specific courses :
- Grokking Coding Interview Patterns in Python
- Grokking Coding Interview Patterns in JavaScript
- Grokking Coding Interview Patterns in Java
- Grokking Coding Interview Patterns in Go
- Grokking Coding Interview Patterns in C++
Available in multiple languages, these courses teach you the underlying patterns for any coding interview question .
This is coding interview prep reimagined , with your needs in mind.
Happy learning
Continue reading about coding interview prep and interview tips #
- The Definitive Guide to Amazon Coding Interviews
- 3 Month Coding Interview Preparation Bootcamp
- "Why Amazon?” How to Answer Amazon’s Trickiest Interview Question
- How to prepare for the System Design Interview
- System Design Interview Questions
Frequently Asked Questions
How to crack Amazon Interview?
Understand the fundamentals of data structures and algorithms, as Amazon interviews often involve complex problem-solving. Practice coding regularly. Check out the previous Amazon coding interview questions and practice well with them.
Is Amazon coding interview hard?
Amazon coding interviews are very interesting yet difficult to ace. In order to do well, it is crucial to have in-depth knowledge and understanding of data structures and algorithms.
What are the different rounds of the Amazon interview?
Amazon’s hiring process includes six key stages:
Resume review Initial phone interviews A meeting with the hiring manager A writing assessment A series of loop interviews Evaluations by the hiring committee
The most challenging phases are the phone screenings, which can take one or two rounds, and the on-site interviews, which involve four to five rounds.
Free Resources
Learn in-demand tech skills in half the time
Mock Interview
Skill Paths
Assessments
Learn to Code
Tech Interview Prep
Generative AI
Data Science
Machine Learning
GitHub Students Scholarship
Early Access Courses
For Individuals
Try for Free
Gift a Subscription
Become an Author
Become an Affiliate
Earn Referral Credits
Cheatsheets
Privacy Policy
Cookie Policy
Terms of Service
Business Terms of Service
Data Processing Agreement
Grokking the Modern System Design Interview
Grokking the Product Architecture Design Interview
Grokking the Coding Interview Patterns
Machine Learning System Design
Copyright © 2024 Educative, Inc. All rights reserved.
Protect your data
This site uses cookies and related technologies for site operation, and analytics as described in our Privacy Policy . You may choose to consent to our use of these technologies, reject non-essential technologies, or further manage your preferences.
- The Top 23 Amazon Interview...
The Top 23 Amazon Interview Questions (With Sample Answers)
9 min read · Updated on November 07, 2024

Prep for your interview with these Amazon interview questions & tips.
Landing an interview with Amazon might feel like one of the most exciting – and intimidating – things to happen to you. Amazon, like most organizations, puts a lot of effort into hiring the right fit for their open positions. As former CEO Jeff Bezos once shared, “I'd rather interview 50 people and not hire anyone than hire the wrong person.”
It says a lot if your resume got past the gatekeepers and into the hands of a hiring manager. Now, take a deep breath and get prepped to answer some of the most common Amazon interview questions.
How to answer Amazon interview questions
From the lengthy list of interview questions that Amazon candidates share online, you can expect that an Amazon interview will rely heavily on situational and behavioral interview questions .
Behavioral interview questions focus on past behavior as an indication of future job success, while situational interview questions ask how you would handle any number of hypothetical situations.
With these questions, you can also pull from past experiences to answer how you would handle the hypothetical situation today or in the future. From there, you can break behavioral and situational interview questions down further into competencies, such as leadership and communication.
To help you answer these types of questions, it's helpful to:
Use the STAR method
Be clear on what value you bring to the job
Using the STAR method during an interview is an excellent approach to answering these types of questions:
Situation: Set the stage by describing the situation.
Task: Describe the task.
Action: Describe the action(s) you took to handle the task.
Results: Share the results achieved.
Be clear on your value and strengths
Some people struggle to share their strengths and the value they can bring to an organization. You need to get over this during your interview if you want to land the job. It's vital that you're able to effectively communicate your strengths, skills, experience, and value you bring to the table to impress the interviewer and help them get a clear understanding of how you can succeed in the role.
Yes, it's true that you don't want to be overly confident or arrogant, though you do want to shine by answering questions in a way that's clear that you have what it takes for the job. To help, make a list of all of your strengths, and refer to those as you practice answering the following Amazon interview questions.
3 Top Amazon interview questions with example answers
Now that you have a foundation on how to answer Amazon interview questions, it's time to practice. Below are three of the top interview questions you are likely to encounter during your interview .
1. What would you do if you found out your closest friend at work was stealing?
You are likely to be asked this question regardless of the position you're interviewing for, especially with cost reduction and shrinkage being top priorities for a company like Amazon. There is really only one way to answer this question that speaks to honesty, integrity, trust, and leadership:
While it would be a difficult situation to find myself in, integrity is essential to me. Plus, stealing is against policy and costs the company's bottom line, no matter how insignificant the theft might seem. I would go to my department manager and report the theft or use the company's recommended reporting policy for such behavior.
2. Describe your most difficult customer and how you handled it.
Amazon is known for their customer service. If the position you're interviewing for is a customer-facing position, then you can count on a question similar to this. When answering this question, apply the STAR method.
Once, I encountered a repeat customer who was upset that an item he ordered was delayed. It was scheduled to arrive within five days of him ordering it, but due to backlog issues with the supplier, the delivery time was adjusted to be 30 days out. The item was an anniversary gift for his wife, and the anniversary was less than two weeks away.
Obviously, the 30 days would not work for him, and he was close to irate about the situation. I needed to figure out a way to help him receive the anniversary gift on time. I first contacted the supplier to see if there was any way to expedite the order, but the best they could do was get the item to him a couple of days earlier than the revised scheduled arrival date.
So, I then worked with the customer to identify a different supplier that sold an almost identical item. I offered him expedited shipping at no charge, so he would receive the item within three days, and that timing worked for his anniversary date. I also offered him a 20 percent coupon towards his next purchase. He was pleased with the outcome, and he remained a loyal customer.
3. Tell me about a time you were 75% through a project and had to pivot quickly. How did you handle it?
Life happens when we are in the middle of projects, and Amazon leadership will want to know how you handle these types of situations when they occur. You could encounter this question for many different types of roles, including technical and management positions. Your answer should speak to your agility, leadership, and problem-solving skills:
At my last job, I was leading a project that was near completion. Everything was moving smoothly and on-target for timely completion. Then, one of our partners providing one of the software upgrades that were to occur at the 90 percent mark encountered a breach of their systems and was estimated to delay the project by two to four weeks.
I had to review our plans and come up with options to keep the project on target as much as possible. Going with another software provider wasn't a viable option, as the groundwork had been laid to go live with the current provider, and starting over would have delayed the project even more. Instead, we were able to allocate two resources to support the provider in recovering from the breach in less than half of the time that was projected.
As a result, we were able to complete the project only two days after the originally scheduled completion date. Fortunately, since we had built in a cushion for contingencies, we were able to go live on schedule.
20 more Amazon interview questions
Below are more possible amazon interview questions you might be asked, broken down into categories. , behavioral questions.
Share about a time when you had a conflict with someone at work. How did you handle it?
Tell me about a time you used innovation to solve a problem.
Tell me about a time when you took a calculated risk. What was the outcome?
Tell me about a time you had to handle a crisis.
Tell me about a time when a team member wasn't pulling their weight. How did you handle it?
Leadership questions
Tell me about a decision you made based on your instincts.
Tell me about a time you used a specific metric to drive change in your department.
Tell me about a time when you influenced change by only asking questions.
What was the last leadership development course you took? What did you gain from it?
Provide an example of a time when you had to complete a project on a budget you felt was too tight. How did you make it work?
Technical and skills questions
How would you improve Amazon's website?
Tell me about how you brought a product to market.
What metrics do you use to influence and drive positive change?
What skills do you possess that will help you succeed at Amazon?
Tell me about a time when you handled a project outside of your scope of work. How did you approach it?
Company-specific questions
Do you know our CEO? How do you spell his name?
How would you introduce Amazon in an elevator pitch?
What are the Amazon leadership principles, and which do you align with most?
What does Amazon's ownership principle emphasize?
Do you know how many Amazon leadership principles there are?
Questions to ask the interviewers
During your Amazon interview, have a list of questions ready to ask your interviewer . Your questions should be company-specific. For example:
What do you feel is the biggest challenge Amazon is currently facing?
What do you love about your role?
How would you describe the team I would be working with?
What is a typical day like in this role?
What qualities are required to succeed at Amazon?
Where do you see Amazon in five years?
Are there any new or unique customer trends you're currently experiencing or projecting?
Tips to land an Amazon interview
If you haven't yet landed an Amazon interview, you'll first need to research and apply for suitable jobs. Here are some tips to help you find an Amazon job online:
Reach out to recruiters on LinkedIn . If your LinkedIn profile is up-to-date and you know what position you're interested in, you can reach out to an Amazon recruiter directly on LinkedIn to inquire about the job.
Request a referral from an Amazon employee. Referrals are a great way to get your foot in the door at an organization. If you know an Amazon employee, consider asking them for a referral for a particular job of interest.
Research and apply through job boards like Indeed . Amazon has several jobs posted on populist job boards for you to explore.
Research and apply through Amazon.jobs . Another option to look for Amazon jobs is to go directly to the source on Amazon's website.
Prepare for Amazon interview questions to land the job!
Amazon interviews are notoriously challenging. But remember, you landed the interview – which puts you one step closer to landing the role.
So, do your homework and take the time to prepare for the interview. Study and practice answering Amazon interview questions, like the ones provided above. Then, you can show them what you've got with confidence once you're in the interview room, which will hopefully lead to that coveted job offer .
Unsure how to answer these interview questions? Our expert interview coaches know how to impress all the major companies you may interview for.
Recommended reading:
Tell Me About Yourself: Examples to Impress in Interviews
How to Research a Company to Find Your Perfect Job Match
How to Answer Interview Questions About Working From Home
Related Articles:
How to Prepare for a Software Engineering Job Interview
27 Financial Analyst Interview Questions (with Great Answers)
27 Supervisor Interview Questions (and Great Answers)
Need a prep talk?
Learn how to crush your interview with confidence.
Share this article:
Questions? We can help.
Our team is standing by, happy to help answer any questions or address any concerns you may have. Just send us your info and we’ll be right in touch. Or, contact us directly:
1-800-803-6018
Thank you! We will be in touch shortly.
01 Beginner
02 questions, amazon interview questions for freshers with answers 2025, what should you expect in amazon interviews, understanding the amazon interview process, common hr interview questions, q 1. tell me about yourself., q 2. why do you want to work at amazon, q 3. what would you say is your biggest strength, q 4. what would you say is your biggest weakness, q 5. can you tell me about a time when you faced a challenge at work, q 6. why did you leave your last job/internship, q 7. where do you see yourself in 5 years, q 8. can you describe a time when you showed leadership, q 9. how do you handle pressure and stress, q 10. how do you prioritize tasks, amazon interview questions for freshers, q 12. can you describe a challenging situation and how you handled it, q 13. how do you prioritize your tasks when you have multiple deadlines, q 14. tell us about a time you worked in a team. what role did you play, q 15. how would you handle a situation where you don’t know the answer to a problem, q 16. what do you know about amazon’s leadership principles, q 17. can you explain a technical concept to someone who doesn’t understand it, q 18. what are your strengths and weaknesses, q 19. how do you stay organized when working on multiple projects, q 20. have you ever disagreed with a team member how did you resolve it, amazon behavioral interview questions, q 21. tell me about a time when you took a risk at work. what was the outcome, q 22. tell me about a time when you disagreed with a supervisor or manager. how did you handle it, q 23. give me an example of a time you showed initiative., q 24. tell me about a time you failed. how did you handle it, q 25. describe a time when you had to manage conflicting priorities. how did you handle it, q 26. tell me about a time when you worked on a team project. what was your role, and how did you contribute, q 27. can you describe a situation where you had to manage multiple tasks under tight deadlines, q 28. tell me about a time when you had to overcome a difficult challenge at work., q 29. describe a situation where you had to make a tough decision. what was the outcome, q 30. tell me about a time when you had to deal with an unhappy customer. how did you resolve the situation, q 31. can you give an example of a time when you had to adapt to a new process or technology, q 32. describe a time when you worked under pressure. how did you manage it, q 33. tell me about a time when you contributed to a project that was outside of your comfort zone., q 34. can you describe a situation where you had to persuade others to adopt your point of view, q 35. tell me about a time you showed leadership without having formal authority., q 36. tell me about a time when you had to quickly learn something new. how did you approach it, q 37. describe a situation where you had to make a decision without all the necessary information. how did you handle it, q 38. tell me about a time when you had to work with someone who was difficult. how did you manage the situation, q 39. tell me about a time when you helped someone improve their performance or skills., q 40. can you describe a time when you had to juggle multiple projects how did you manage them, amazon software developer interview questions, q 41. what is the difference between a stack and a queue, q 42. what is a hash table, and how does it work, q 43. what is the time complexity of binary search, q 44. how do you reverse a linked list, sample code, q 48. how do you implement an lru (least recently used) cache, q 49. what is a linked list, and how does it differ from an array, q 50. what is the time complexity of bubble sort, q 51. what is the purpose of the ‘final’ keyword in java, q 53. how does a quicksort algorithm work, and what is its time complexity, q 54. what is the difference between `==` and `equals()` in java, q 55. what is a deadlock in a multi-threaded application, and how do you prevent it, q 56. what is the purpose of exception handling in programming, q 57. what is a race condition in multi-threading, q 58. how do you implement a priority queue, q 59. how do you avoid memory leaks in java, q 60. what is the difference between `throw` and `throws` in java, q 62. what is the difference between static and non-static methods, q 63. what is the difference between `arraylist` and `linkedlist` in java, q 64. what is the difference between a class and an object, q 65. explain the concept of inheritance in object-oriented programming., q 66. what is a constructor in java, and what is its purpose, q 67. what is the difference between an interface and an abstract class, q 68. what is the purpose of a `final` class in java, q 69. what is multithreading in java, and why is it used, q 70. what are java annotations, and how are they used, q 71. what is the difference between `inner join` and `outer join`, q 72. what is a `group by` clause, and how does it work, q 73. what is the difference between `having` and `where`, q 74. what are aggregate functions in sql, q 75. what is a `subquery` in sql, q 76. what is the difference between `union` and `union all`, q 77. what is the purpose of `index` in sql, q 78. what are the primary key and foreign key, q 79. what is normalization, and why is it important, q 80. what is denormalization, and why is it used, q 81. what is `truncate` and `delete` in sql, q 82. what is `auto_increment` in sql, q 83. explain the `case` statement in sql., q 84. what is a `view` in sql, q 85. what is `limit` in sql, amazon system design interview questions, q 86. design a url shortening service like bit.ly, q 87. design a messaging system like whatsapp., q 88. design a scalable file storage system (like google drive)., q 89. design a rate limiter., q 90. design a recommendation system like amazon's product recommendations, q 91. design a distributed cache system, q 92. design a distributed logging system, q 93. design a voting system, q 94. design a cache eviction policy (least recently used - lru), q 95. design a system for storing and querying billions of rows of data, q 96. design an online multiplayer game backend, q 97. design a search engine like google, q 98. design a system for streaming data (like kafka), q 99. design a global content delivery network (cdn), q 100. design a system for real-time analytics, q 101. design a payment gateway system, amazon data engineer interview questions, q 102: what is the etl process, and how do you design it, q 103: can you explain key data warehousing concepts, q 104: how do you optimize sql queries, q 105: what is the difference between normalization and denormalization, q 106: how does amazon redshift work, and how do you use it, q 107: how would you handle unstructured data, q 108: what strategies do you use to ensure data quality, q 109: can you explain data partitioning and why it’s important, q 110: describe schema design considerations for analytics., q 111: how do you build and scale data pipelines, q 112: describe your experience with big data tools., q 113: how do you handle data security and compliance, q 114: what is the difference between a data lake and a data warehouse, q 115: how does caching improve data access, and where would you use it, simple tips and tricks for cracking amazon interview , q1. what technical skills should i focus on for an amazon interview, q2. how do i approach amazon’s system design questions, q3. what coding languages are preferred in amazon technical interviews, q4. how can i effectively answer amazon's leadership principle questions, q5. are there specific amazon interview questions for data engineers, about author.

- Interview Advice
Using Problem-Solving Situations During Amazon Interviews
Former Amazon senior manager shares proven tips for mastering Amazon's problem-solving interview questions aligned with Leadership Principles.

If you join Amazon, you will quickly realize that everyone around you is a serial problem solver. This is by design. Besides being an organization of over-achievers, Amazon has a profoundly ingrained engineering ethos that lives in tech and non-tech organizations.
Therefore, you won’t be surprised that problem-solving is a recurring theme throughout the interview process. Amazon behavioral interview questions that ask you to share a situation where you were solving problems map to 5 out of 16 Leadership Principles. Problem-solving questions can test Dive Deep, Invent & Simplify, Are Right A Lot, Frugality, and Learn & Be Curious.
However, unless you know the nuances of the Leadership Principles, we can’t blame you for being somewhat confused about what LP is being tested in one problem-solving question or another. Another complication for candidates is that when we find ourselves in real-life problem-solving situations, we may demonstrate a range of leadership principles mixed.
We wrote this article to offer you a quick orientation around problem-solving themes in Amazon Leadership Principles and the interview questions that test them. We hope it will make it easier for you to pick the right situation during the interview and focus on the correct details to answer Amazon interview questions.
Problem-solving and Dive Deep
While Amazon's Dive Deep Leadership Principle is not only about problem-solving, some Dive Deep questions will look for evidence of your ability to solve complex problems. Of course, complexity means different things to different people. Yet, in an Amazon interview context, it typically boils down to three things.
- A problem that requires multiple levels of data analysis (peeling the data onion) to solve.
- A problem had you using numerous data sources (from either systems or people) to find a solution.
- A problem was so novel that it took a while to figure out how to approach it.
In contrast to other Leadership Principle questions that ask for problem-solving evidence, the main focus of Dive Deep is on the process of getting to the solution itself. Here, we’d recommend that you focus on establishing the source of complexity and then outline the steps you took to get to the very bottom of the problem.
Problem-solving and Invent & Simplify
At the heart of the Invent and Simplify Leadership principle at Amazon are two distinct themes: invention and simplification, as the name of the LP suggests. Problem-solving typically comes under the Simplification theme.
Under Invent and Simplify, Amazon will expect you to demonstrate how you effectively boiled complexity into simplicity while solving a problem. From our experience at Amazon, we can attest that many problems started as giant hairy monsters with unknown root causes and hidden under a sea of data (most of which was useless to the analysis).
While you should still follow a STAR format of answering Amazon Leadership Principle questions, Invent and Simplify problem-solving responses should focus on the “A-Ha!” moment that led you to invent a simple solution. The invention of a fix at the end of the problem-solving journey is the main currency of an acceptable answer. Therefore, the bulk of your story-telling should detail the innovation process rather than digging for the root cause.
Problem-solving and Are Right A Lot
Are Right; A Lot of Leadership Principle at Amazon is mainly about continuously learning from your successes and failures to always make the right decisions. So, where does problem-solving feature in this LP? Very prominently. Just think about when you need to solve a problem while operating under uncertainty or, perhaps, without having all the knowledge and expertise right away. So, being able to inform your gut on the spot by learning from people and systems around you is how you would need to approach problem-solving under Are Right A Lot.
Therefore, the currency of a good problem-solving answer to the Are Right A Lot Leadership Principle question in an Amazon interview is a series of steps of how you went about building or disconfirming (challenging) your beliefs while operating under uncertainty and needing to solve a problem.
Problem-solving and Frugality
If you’ve taken our training ( Amazon Interview Whizz ), you will remember the main themes of the Frugality Leadership Principle at Amazon. Having read the previous few sections, you won’t be surprised that Frugality situations may also have a problem-solving element.
But this time, you are operating under resource constraints and have to do with what you have. This is Frugality, defined by the official version (achieve more with less), but just in a problem-solving contest.
Hence, the currency of a decent problem-solving answer to Amazon interview questions on the Frugality Leadership Principle would be a story about how you effectively ran with what you had to solve a challenge.
Problem-solving and Learn & Be Curious
Problem-solving themes under Learn & Be Curious are similar to those under Are Right. The slight difference is in the nuances. While Are Right A Lot is about drawing on the expertise of others to inform or challenge your intuition, Learn & Be Curious is about acquiring knowledge. Both Leadership Principles make one a confident problem-solver, and you have probably demonstrated both LPs in real-life situations, possibly both simultaneously. However, in an Amazon interview situation, it would be helpful to focus your response on the details that matter for Learn & Be Curious.
Therefore, the currency of a workable answer under this Leadership Principle in an Amazon interview is a story of the steps you took to acquire expertise that you did not have to solve a problem.
We hope this article helped you understand the nuances of sharing problem-solving situations when answering Leadership Principles questions in behavioral interviews at Amazon. If you fancy taking your interview preparation to the next level, check out Amazon Interview Whizz , our signature training course. It is based on our insights from thousands of interviews, coaching sessions, and hiring decisions.

Mastering the "Why Amazon" Interview Question: Strategies and Sample Answers

Amazon Interview Preparation: A Comprehensive Guide to Success

Top Questions to Ask a Hiring Manager During Your Interview

Crafting Your Answer: Nailing Why Do You Want to Work Here? in Interviews

Navigating Expected Salary Questions Like a Pro

Mastering the Marketing Interview: Conquering Behavioral Questions

COMMENTS
What are the most common types of technical questions asked in an Amazon SDE interview? Amazon SDE interviews commonly feature questions on data structures, algorithms, coding problems, and system design. These assess a candidate’s problem-solving skills and technical knowledge. How important are Amazon’s leadership principles in the ...
Today, we’ll walk you through everything you need to crack the Amazon technical interview, including questions and answers for coding problems and a step-by-step tech interview prep guide. Amazon Leetcode Questions #
Solve the most popular amazon interview questions. Prepare for DSA interview rounds at the top companies.
What questions do Amazon interviewers ask? In this post, our experts cover the top 23 Amazon interview questions with example responses and tips!
Problem-solving skills: Be prepared to show how you break down complex problems and find efficient solutions. You may face real-world scenarios. Amazon's Management Principles: Expect questions about Amazon's ideals, such as customer focus, ownership, and streamlining procedures.
Amazon behavioral interview questions that ask you to share a situation where you were solving problems map to 5 out of 16 Leadership Principles. Problem-solving questions can test Dive Deep, Invent & Simplify, Are Right A Lot, Frugality, and Learn & Be Curious.