Design thinking

Design thinking is an iterative process that involves empathizing with users, defining problems from their perspective, ideating solutions, prototyping ideas, and testing prototypes with users. It focuses on understanding user needs through observation and interviews to identify root problems. Potential solutions are then explored through brainstorming techniques and low-fidelity prototyping before gathering user feedback through testing techniques like card sorting and the "Wizard of Oz" method to further refine solutions. The goal is to generate a wide range of ideas and learn through iterative prototyping and user testing. Read less


More Related Content
- 1. Design thinking
- 2. What is Design Thinking • Design Thinking is an iterative process in which we seek to • understand the user • challenge assumptions • redefine problems in an attempt to • identify alternative strategies and solutions that might not be instantly apparent with our initial level of understanding. • At the same time, Design Thinking provides a solution-based approach to solving problems. It is a way of thinking and working as well as a collection of hands-on methods.
- 3. • the more I pondered the nature of design and reflected on my recent encounters with engineers, business people and others who blindly solved the problems they thought they were facing without question or further study, I realized that these people could benefit from a good dose of design thinking.[… ] • Most important of all, is that the process is iterative and expansive. Designers resist the temptation to jump immediately to a solution to the stated problem. Instead, they first spend time determining what the basic, fundamental (root) issue is that needs to be addressed. They don't try to search for a solution until they have determined the real problem, and even then, instead of solving that problem, they stop to consider a wide range of potential solutions. Only then will they finally converge upon their proposal. This process is called "Design Thinking. Don Norman
- 6. Some authors are less optimistic when considering the amount of iteration required
- 7. Empathize • “deep understanding of the problems and realities of the people you are designing for” • 3 steps • Observe • How users interact with their environment. • Capture quotes, behaviors and other notes that reflect their experience. • Notice what they think, feel, need • Engage • Interviews scheduled or ad-hoc • Learn how to ask the right questions • Immerse • Find ways “to get into the user’s shoes” • Best way to understand the users’ needs
- 8. Empathize tools • Assume a beginner’s mindset • Ask What-How-Why • Ask the 5 whys • Empathy map • Conduct interviews with empathy • Build empathy with analogies • Use photo and video user-based studies • Use personal photo and video journals • Engage with extreme users • Story share-and-capture • Bodystorm • Create journey maps
- 9. Empathize - Beginner’s mindset • Forget your assumptions and personal beliefs • Misconceptions or stereotypes limit the amount of real empathy you can build. • A beginner’s mindset allows you • to put aside biases and approach • Design with fresh eyes • What you should do • Don’t judge • Question everything • Be truly curious • Find patterns • Listen without thinking how you’re going to respond
- 10. Empathize – Ask What – How - Why • Tool to help you better observe • Especially good for analysing photos • What you should do for a specific observation • Divide a sheet into 3 parts – What / How / Why • What = write what you observe the user is doing without making assumptions • How = understand what the user is doing. Is it positive or negative, does it require effort? Use plenty of adjectives • Why = now you have to interpret; guess motivations and emotions, make assumptions that you have to test with users later
- 11. Empathize – Ask the 5 whys • Repeating the Why question 5 times to identify the root cause of a problem • Some useful rules • Write down the problem and make sure that all people understand it. • Distinguish causes from symptoms. • Pay attention to the logic of cause-and-effect relationship. • Assess the process, not people. • Never leave "human error", "worker's inattention", "blame John" etc., as the root cause. • When you form the answer for question "Why" - it should happen from the customer's point of view.
- 12. Empathize – Empathy map • Says • quotes from what users say during interview • Thinks • What users seem to think when experiencing the product • Does • Actions that the user takes during the experiment • Feels • The user’s emotional state (adjective + context) like Impatient: pages load too slowly
- 15. Empathize – Conduct interviews with empathy • Ask why. • Never say “usually” when asking a question. • Encourage stories • Look for inconsistencies. • Pay attention to nonverbal cues. • Don’t be afraid of silence. • Ask questions neutrally and don’t suggest answers.
- 16. Empathize - Build empathy with analogies • Use analogies to gain a fresh way of looking at an environment, and in instances where direct observation is hard to achieve. • analogies allow us to express our ideas or to explain complex matters in an understandable and motivating way. • Start by identifying the aspects of a situation that are most important, interesting, or problematic. • Find other experiences that contain some of these aspects — it will help you gain a better understanding of your users’ problems, and it will also spark new ideas to improve their experiences. • Create an inspiration space for analogies. You can do so by pinning photos and anecdotes of the analogous experiences you have found.
- 17. Empathize - Use photo and video user-based studies • Use video recordings of users performing their regular activities • Try to make the study as casual as possible so that the user doesn’t feel any pressure • Use different techniques like how-what-why to examine the videos or photos or frames taken from the videos
- 18. Empathize - Engage with extreme users • Determine who’s extreme. • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5R3pKV9ucBc&t=607s • Engage. • Observe and interview extreme users just like other folks. Look for work- arounds (or other extreme behaviors) to spark inspiration and uncover insights. • Look at the extreme in all of us. • Look to extreme users to spur wild ideas. Then narrow in on what resonates with the primary users that you’re designing for.
- 19. Empathize - Bodystorm • Bodystorming is a unique method that spans empathy work, ideation, and prototyping. • technique of physically experiencing a situation to derive new ideas. • requires setting up an experience - complete with necessary artifacts and people - and physically “testing” it. • can include physically changing your space during ideation. • you're focused on here is the way you interact with your environment and the choices you make while in it. • Example: when thinking about a product for blind people try to actually experiment not using your eyes during an experiment and try to see what you can achieve and what are your needs
- 20. Empathize - Create journey maps • Visual representation of the process a customer or prospect goes through to achieve a goal with your company/products • Identity the customer’s needs and pain points • Steps: • Set clear objectives for the map. • Profile your personas and define their goals. • List out all the touchpoints (places in the app/site where you can interact with the customer) • Identify the elements you want your map to show. • Take the customer journey yourself. • Make necessary changes.
- 23. Define • synthesise your observations about your users from the Empathize stage • definition of a meaningful and actionable problem statement, which the design thinker will focus on solving • A great definition of your problem statement => kick start the ideation process (third stage) in the right direction. • unpack your empathy findings into needs and insights and scope a meaningful challenge • Define your Point of View – meaningful and actionable problem statement • Preserves emotion and the individual you’re designing for. • Includes strong language. • Uses sensical wording. • Includes a strong insight. • Generates lots of possibilities
- 24. Define tools • Point of view • How Might We • Why-How Ladder • Powers of Ten
- 25. Define - Point of View • You articulate a POV by combining these three elements – user, need, and insight. • insert your information about your user, the needs and your insights in the following sentence: • [User . . . (descriptive)] needs [need . . . (verb)] because [insight. . . (compelling)]
- 26. Define - How might we? • Short questions that launch brainstorms • Seeds for ideation • Come out form the point of view statement • Example: • Challenge: Redesign the ground experience at the local international airport • POV: Harried mother of three, rushing through the airport only to wait hours at the gate, needs to entertain her playful children because “annoying little brats” only irritate already frustrated fellow passengers. • (https://dschool- old.stanford.edu/sandbox/groups/dstudio/wiki/2fced/attachments/f6 3e8/How-Might-We-Questions-Method.pdf)
- 27. Define - How might we • Amp up the good: HMW use the kids’ energy to entertain fellow passenger? • Remove the bad: HMW separate the kids from fellow passengers? • Explore the opposite: HMW make the wait the most exciting part of the trip? • Question an assumption: HMW entirely remove the wait time at the airport? • Go after adjectives: HMW we make the rush refreshing instead of harrying? • ID unexpected resources: HMW leverage free time of fellow passengers to share the load? • Create an analogy from need or context: HMW make the airport like a spa? Like a playground? • Play against the challenge: HMW make the airport a place that kids want to go? • Change a status quo: HMW make playful, loud kids less annoying? • Break POV into pieces: HMW entertain kids? HMW slow a mom down? HMW mollify delayed passengers?
- 28. Define - Why How Ladder • Used to find user needs and ways to possibly solve them • Step 1: Identify a few meaningful user needs and write them at the bottom of a piece of paper. • Step 2 Ladder up from that need, asking “why?” • For example, why would a user “need to see a link between a product and the process that creates it?” because the user, “needs confidence that it won’t harm their health by understanding its origin.” • Step 3 Ask why again, and continue to ladder from that same need. • At a certain point, you’ll reach a very common, abstract need such as, “the need to be healthy.” This is the top of the ladder. • Step 4 Climb back down the ladder asking “how?” • This will give you ideas for how to address the needs
- 29. Ideate • generate radical design alternatives • The goal of ideation is to explore a wide solution space • both a large quantity and broad diversity of ideas. • From this pool of ideas you can build prototypes to test with users
- 30. How to ideate • Ideate=transition from identifying problems to exploring solutions • Ideation is leveraged to: • Harness the collective perspectives and strengths of your team. • Step beyond obvious solutions and drive innovation. • Uncover unexpected areas of exploration. • Create fluency (volume) and flexibility (variety) in your innovation options. • Fluctuate between focus and flare
- 31. Tools to ideate • Brainstorm • Braindump • Brainwrite • Brainwalk • Challenge Assumptions • SCAMPER • Mindmap • Sketch or Sketchstorm • Storyboard • Analogies • Provocation • Movement • Bodystorm • Gamestorming • Cheatstorm • Crowdstorm • Co-Creation Workshops • Power of Ten • Prototype • Creative Pause
- 32. Ideate - Brainwrite • the participants write down their ideas on paper • they pass on their own piece of paper to another participant • The other participant elaborates on the first person’s ideas and so forth. • Another few minutes later, the individual participants will again pass their papers on to someone else and so the process continues. • The process takes 15 minutes • Ideas are discussed afterwords
- 33. Ideate – Challenge Assumptions • Identify the assumptions you have about the product you’re building • (especially if you’re stuck) • Challenge these assumptions • Are they fixed because they are crucial aspects or because we have been accustomed to them? • Very important step if the empathy stage wasn’t well done and there were many things assumed about the users and their context
- 34. Ideate - Mindmap • Process through which the participants build a web of relationships • Participants write a problem statement • They write solutins • Link statements and solutions between them
- 36. Ideate – Creative pause • (I’d really hope to manage to sync this slide with the course break)
- 37. Define/Ideate – Power of Ten • Consider challenges through frames of various magnitudes • Consider increasing and decreasing magnitudes of context to reveal connections and insights. • Powers of ten for insight development – imagine what happens for example when shopping for bubble gum vs. shopping for a TV vs. shopping for a house • How does this changes the user behaviour? • Powers of ten for ideation • Add constraints that alter the magnitude of the solution space (cost of 1 mil $ vs. 1 cent)
- 38. Prototype • A prototype can be anything that takes a physical form—a wall of post-its, a role-playing activity, an object. • In early stages, keep prototypes inexpensive and low resolution to learn quickly and explore possibilities. • Prototypes are most successful when people (the design team, users, and others) can experience and interact with them. • great way to start a conversation. • interactions with prototypes drives deeper empathy and shapes successful solution
- 39. Low fidelity prototyping • use basic models or examples • Just some features • Methods • Storyboarding. • Sketching • Card sorting. • 'Wizard of Oz'.
- 40. Low fidelity prototyping • Pros • Quick and inexpensive. • Possible to make instant changes and test new iterations. • Disposable/throw-away. • Enables the designer to gain an overall view of the product using minimal time and effort, • No advanced technical skills required • Encourages and fosters design thinking. • Cons • lack of realism. basic and sometimes sketchy nature =>the applicability of results may lack validity. • Depending on your product, the production of low-fi prototypes may not be appropriate for your intended users. • Such prototypes often remove control from the user, as they generally have to interact in basic ways or simply inform an evaluator, demonstrate or write a blow-by-blow account of how they would use the finished product.
- 41. High fidelity prototyping • look and operate closer to the finished product • For example, a 3D plastic model with movable parts (allowing users to manipulate and interact with a device in the same manner as the final design) is high-fi in comparison to, say, a wooden block. • Likewise, an early version of a software system developed using a design program such as Sketch or Adobe Illustrator is high-fi in comparison to a paper prototype.
- 42. High fidelity prototyping • Pros • Engaging: the stakeholders can instantly see their vision realised and will be able to judge how well it meets their expectations, wants and needs. • User testing involving high-fi prototypes will allow the evaluators to gather information with a high level of validity and applicability. The closer the prototype is to the finished product, the more confidence the design team will have in how people will respond to, interact with and perceive the design. • Cons • They generally take much longer to produce than low-fi prototypes. • When testing prototypes, test users are more inclined to focus and comment on superficial characteristics, as opposed to the content • After devoting hours and hours of time producing an accurate model of how a product will appear and behave, designers are often loathed to make changes. • Software prototypes may give test users a false impression of how good the finished article may be. • Making changes to prototypes can take a long time
- 43. Test • chance to gather feedback, refine solutions, and continue to learn about your users. • The test mode is an iterative mode in which you place low-resolution prototypes in the appropriate context of your user’s life. • Prototype as if you know you’re right, but test as if you know you’re wrong
- 44. Prototype/Test – Wizard of Oz Prototyping • A wizard of Oz prototype fakes functionality that you want to test with users, saving you the time and money of actually creating it. • prototypes of digital systems, in which the user thinks the response is computer-driven, when in fact it’s human-controlled. • Determine what you want to test. • Then figure out how to fake that functionality and still give users an authentic experience
- 45. Prototype/Test – Card sorting • how concepts for a project should be organized • help the user experience professional know how to best organize a website or software application so that the structure of information will be logical for the largest number of users. • Open card sorting = asking the users to come up with category names for each card • Closed card sorting = predefined names for each category • a participant is given a number of cards or sticky notes, each containing a different word. The test participant is then asked to organize these as he sees best
- 46. Testing with users • Allows you to learn about the solution you created but also about the users (builds empathy) • Let your user experience the prototype. • Show don’t tell. Put your prototype in the user’s hands (or your user in the prototype) and give only the basic context they need to understand what to do. • Have them talk through their experience. • Use prompts. “Tell me what you’re thinking as you do this.” • Actively observe. • Don’t immediately “correct” your user. • Watch how they use (and misuse) your prototype. • Follow up with questions. • This is often the most valuable part.
- 47. Test – Feedback capture matrix • real-time capture of feedback on presentations and prototypes • arranges thoughts and ideas into four categories for easy assessment • Fill in the matrix as you give or receive feedback. • 1st quadrant: Constructive criticism • 2nd quadrant: Place things one likes or finds notable • 3rd quadrant: Questions raised • 4th quadrant: new ideas spurred
- 48. Bibliografie • https://www.interaction-design.org/literature/article/what-is-design-thinking-and-why- is-it-so-popular • Stanford dschool Design Thinking Bootleg - https://static1.squarespace.com/static/57c6b79629687fde090a0fdd/t/5b19b2f2aa4a99e 99b26b6bb/1528410876119/dschool_bootleg_deck_2018_final_sm+%282%29.pdf • Design Thinking 101 - https://media.nngroup.com/media/articles/attachments/Design- thinking-101-NNG.pdf • https://hbr.org/2018/09/why-design-thinking-works • How to Create an Effective Customer Journey Map [Examples + Template] • Bodystorm | Interaction Design Foundation • Building Empathy with Analogies - Building-Empathy-with-Analogies.pdf • Bodystorming | Design Research Techniques • https://pidoco.com/en/help/ux/card-sorting
Editor's Notes
- Don’t judge. Observe and engage users without the influence of value judgments Question everything. Even (and especially) the things you think you already understand. Ask questions to learn about the world from the user’s perspective. Be truly curious. Strive to assume a posture of wonder and curiosity, both in circumstances that seem either familiar or uncomfortable. Find patterns. Look for interesting threads and themes that emerge across user interactions. Listen. Really. without thinking about how you’re going to respond.
- The Says quadrant contains what the user says out loud in an interview or some other usability study. Ideally, it contains verbatim and direct quotes from research. “I am allegiant to Delta because I never have a bad experience.” “I want something reliable.” “I don’t understand what to do from here.” The Thinks quadrant captures what the user is thinking throughout the experience. Ask yourself (from the qualitative research gathered): what occupies the user’s thoughts? What matters to the user? It is possible to have the same content in both Says and Thinks. However, pay special attention to what users think, but may not be willing to vocalize. Try to understand why they are reluctant to share — are they unsure, self-conscious, polite, or afraid to tell others something? “This is really annoying.” “Am I dumb for not understanding this?” The Does quadrant encloses the actions the user takes. From the research, what does the user physically do? How does the user go about doing it? Refreshes page several times. Shops around to compare prices. The Feels quadrant is the user’s emotional state, often represented as an adjective plus a short sentence for context. Ask yourself: what worries the user? What does the user get excited about? How does the user feel about the experience? Impatient: pages load too slowly Confused: too many contradictory prices Worried: they are doing something wrong
- Ask why - Even when you think you know the answer. Never say usually - Instead, ask about a specific occurrence. “Tell me about the last time you ____.” Encourage stories. Stories reveal how users think about the world. Look for inconsistencies. What users say and do can be different. These inconsistencies often hide interesting insights. Pay attention to nonverbal cues. Be aware of body language and emotions. Don’t be afraid of silence. When you allow for silence, you give users time to reflect on their answers— which may lead to deeper responses. Q neutrally: “What do you think about buying gifts for your spouse?” is better than “Don’t you think shopping is great?”
- An analogy is a comparison between two things—for example, a comparison of a heart to a pump. Ce comparatii relevante gasim in lumea inconjuratoare, comparatii care ne pot inspira in designul unui produs.
- For instance, if you are developing a product bound by a number of contextual constraints and/or dispositional constraints (i.e. physical characteristics of your user base, such as users with disabilities) then basic versions that do not reflect the nature, appearance or feel of the finished product may be of scant use; revealing very little of the eventual user experience.
Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches

15 templates

girls night
13 templates

happy new year
21 templates

106 templates

merry christmas
22 templates

pharmaceutical industry
34 templates
All About Design Thinking
It seems that you like this template, all about design thinking presentation, premium google slides theme, powerpoint template, and canva presentation template.
Download the All About Design Thinking presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides and start impressing your audience with a creative and original design. Slidesgo templates like this one here offer the possibility to convey a concept, idea or topic in a clear, concise and visual way, by using different graphic resources. You need to talk about a specific topic, but you don't know how to do it? Try using presentations like this one here, 100% customizable!
Features of this template
- 100% editable and easy to modify
- Different slides to impress your audience
- Contains easy-to-edit graphics such as graphs, maps, tables, timelines and mockups
- Includes 500+ icons and Flaticon’s extension for customizing your slides
- Designed to be used in Google Slides and Microsoft PowerPoint
- Includes information about fonts, colors, and credits of the resources used
What are the benefits of having a Premium account?
What Premium plans do you have?
What can I do to have unlimited downloads?
Don’t want to attribute Slidesgo?
Gain access to over 31100 templates & presentations with premium from 1.67€/month.
Are you already Premium? Log in
Create your presentation Create personalized presentation content
Writing tone, number of slides.

Register for free and start downloading now
Related posts on our blog.

How to Add, Duplicate, Move, Delete or Hide Slides in Google Slides

How to Change Layouts in PowerPoint

How to Change the Slide Size in Google Slides
Related presentations.

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access

Register for free and start editing online
JavaScript seems to be disabled in your browser. For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Javascript in your browser.
Newly Launched - AI Presentation Maker

AI PPT Maker
Powerpoint Templates
PPT Bundles
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories
Top 10 Designs Thinking PowerPoint Presentation Templates in 2024
Design Thinking is a human-centered approach to innovation that emphasizes understanding the needs and experiences of users. It involves a series of stages, including empathy, definition, ideation, prototyping, and testing, which guide teams in developing solutions that are not only creative but also practical. Utilizing PowerPoint (PPT) templates designed for Design Thinking can greatly enhance the effectiveness of workshops and presentations aimed at fostering collaboration and brainstorming.These PPT templates provide a structured framework that helps teams visualize their ideas and processes clearly. For instance, during the empathy stage, teams can use slides to capture user insights, quotes, and personas, making it easier to understand the target audience's needs. In the ideation phase, customizable slides can facilitate brainstorming sessions by allowing participants to jot down ideas quickly and organize them visually. Prototyping can be presented through interactive slides that showcase potential solutions, while the testing phase can include feedback forms and evaluation metrics.By leveraging these PPT templates, teams can streamline their Design Thinking processes, encourage participation, and foster an environment of creativity and innovation. Ultimately, these tools not only enhance communication but also ensure that the focus remains on delivering user-centered solutions that address real-world challenges.
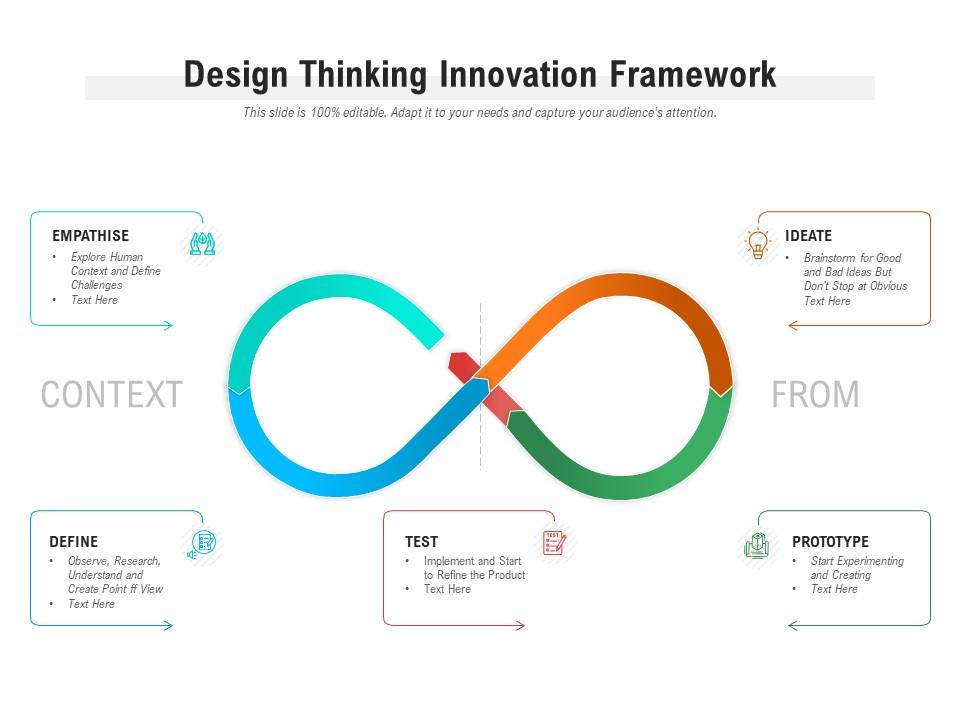
Design thinking innovation framework
Presenting this set of slides with name Design Thinking Innovation Framework. This is a five stage process. The stages in this process are Empathise, Define, Test, Prototype, Ideate. This is a completely editable PowerPoint presentation and is available for immediate download. Download now and impress your audience.
Indicate your joy with our Design Thinking Innovation Framework. Convey happiness on their achievement.
Related Products
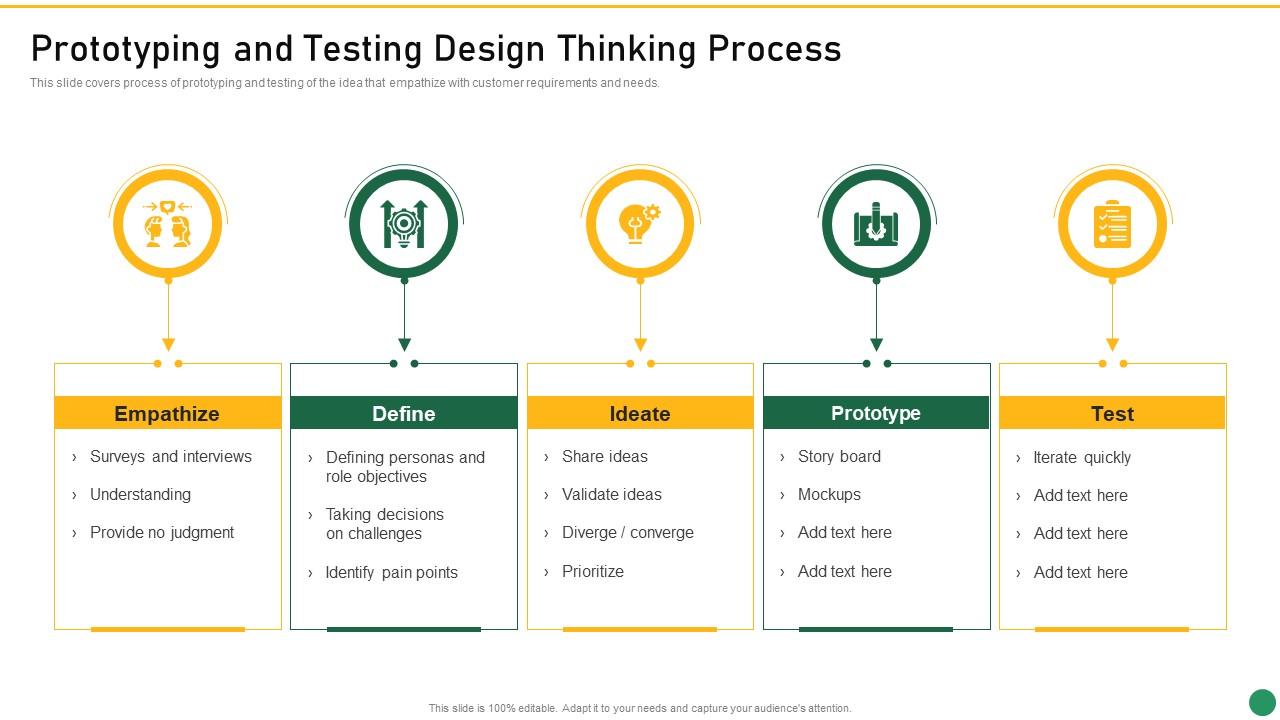
Prototyping And Testing Design Thinking Process Set 1 Innovation Product Development
This slide covers process of prototyping and testing of the idea that empathize with customer requirements and needs. Introducing Prototyping And Testing Design Thinking Process Set 1 Innovation Product Development to increase your presentation threshold. Encompassed with five stages, this template is a great option to educate and entice your audience. Dispence information on Surveys And Interviews, Understanding, Provide No Judgment, Defining Personas And Role Objectives, Taking Decisions On Challenges, using this template. Grab it now to reap its full benefits.
This slide covers process of prototyping and testing of the idea that empathize with customer requirements and needs.
- Surveys And Interviews
- understanding
- Provide No Judgment
- Defining Personas And Role Objectives
- Taking Decisions On Challenges
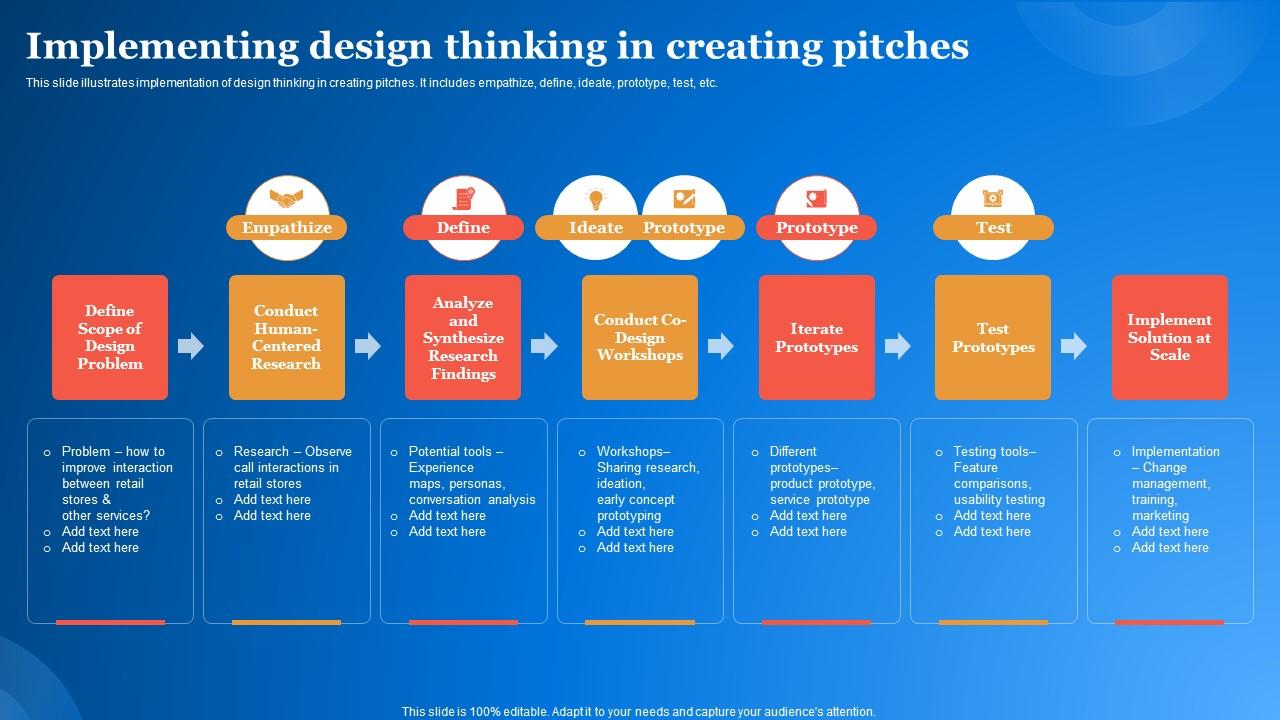
Implementing Design Thinking In Creating Pitches
This slide illustrates implementation of design thinking in creating pitches. It includes empathize, define, ideate, prototype, test, etc. Presenting our set of slides with name Implementing Design Thinking In Creating Pitches. This exhibits information on seven stages of the process. This is an easy to edit and innovatively designed PowerPoint template. So download immediately and highlight information on Iterate Prototypes, Test Prototypes, Research Findings.
This slide illustrates implementation of design thinking in creating pitches. It includes empathize, define, ideate, prototype, test, etc.
- Iterate Prototypes
- Test Prototypes
- Research Findings

Implementing Design Thinking Powerpoint Ppt Template Bundles
Introduce your topic and host expert discussion sessions with this Implementing Design Thinking Powerpoint Ppt Template Bundles. This template is designed using high-quality visuals, images, graphics, etc, that can be used to showcase your expertise. Different topics can be tackled using the seventeen slides included in this template. You can present each topic on a different slide to help your audience interpret the information more effectively. Apart from this, this PPT slideshow is available in two screen sizes, standard and widescreen making its delivery more impactful. This will not only help in presenting a birds-eye view of the topic but also keep your audience engaged. Since this PPT slideshow utilizes well-researched content, it induces strategic thinking and helps you convey your message in the best possible manner. The biggest feature of this design is that it comes with a host of editable features like color, font, background, etc. So, grab it now to deliver a unique presentation every time.
Our Implementing Design Thinking Powerpoint Ppt Template Bundles are topically designed to provide an attractive backdrop to any subject. Use them to look like a presentation pro.
- Implementing Design Thinking Mindset
- Design Thinking Implementation
- Business Innovation Design Thinking
- Business Thinking Vs Design Thinking
Design Thinking Creative Cycle Colored Icon In Powerpoint Pptx Png And Editable Eps Format
This Creative Cycle PowerPoint Icon is a vibrant and colourful graphic that can be used to illustrate the concept of a creative cycle. It features a multicoloured wheel with arrows pointing inwards, making it perfect for presentations and web projects.
Use this Design thinking creative cycle colored icon in powerpoint pptx png and editable eps format and create amazing PowerPoint presentations or graphics with ease. This downloaded file is available in all the editable formats such as EPS, PNG and Powerpoint pptx.
- Creative Process
- brainstorming
- design thinking

Design Thinking Framework Analysis Inspirational Service Innovation
This complete deck can be used to present to your team. It has PPT slides on various topics highlighting all the core areas of your business needs. This complete deck focuses on Design Thinking Framework Analysis Inspirational Service Innovation and has professionally designed templates with suitable visuals and appropriate content. This deck consists of total of twelve slides. All the slides are completely customizable for your convenience. You can change the colour, text and font size of these templates. You can add or delete the content if needed. Get access to this professionally designed complete presentation by clicking the download button below.
Our Design Thinking Framework Analysis Inspirational Service Innovation are topically designed to provide an attractive backdrop to any subject. Use them to look like a presentation pro.
- inspirational

Effective Design Thinking Training Program
This slide showcases the major design thinking training courses for employees. It include details such as design thinking for innovative ideas, etc. Introducing our Effective Design Thinking Training Program set of slides. The topics discussed in these slides are Innovative Ideas, Design Overview, Project Management. This is an immediately available PowerPoint presentation that can be conveniently customized. Download it and convince your audience.
This slide showcases the major design thinking training courses for employees. It include details such as design thinking for innovative ideas, etc.
- innovative ideas
- Design Overview
- project management
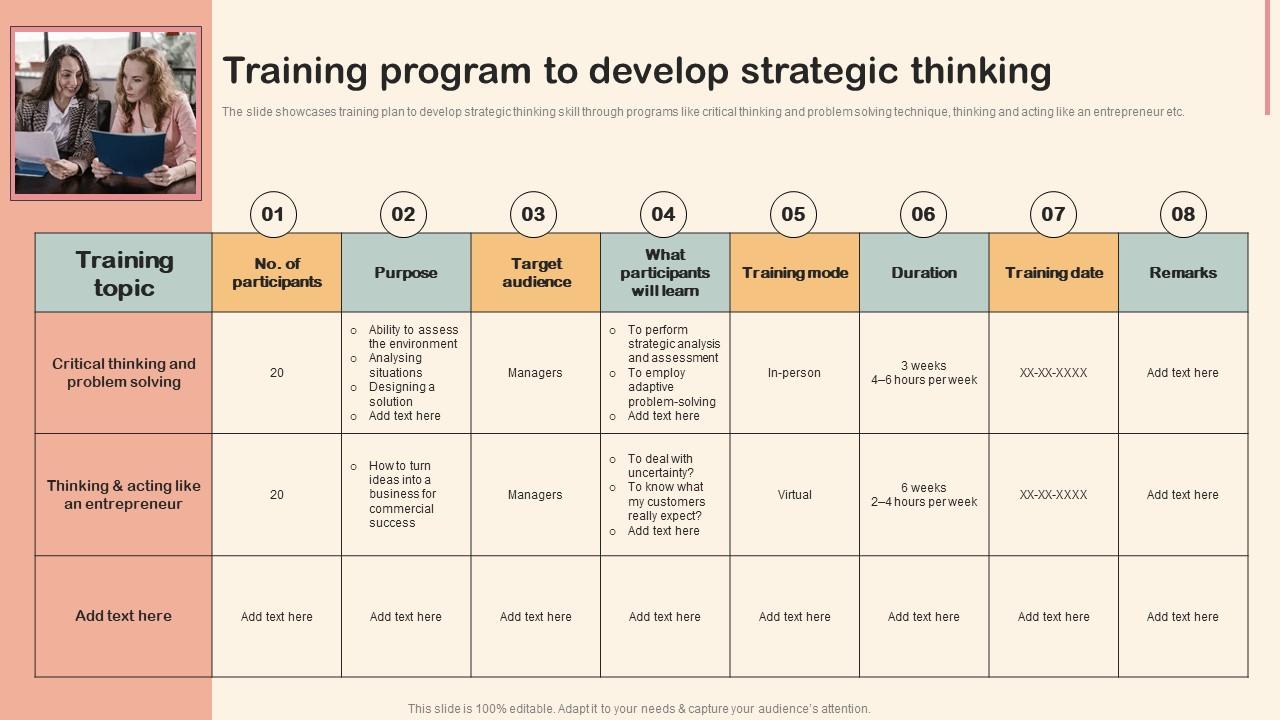

Training Program To Develop Strategic Thinking Professional Development Training
The slide showcases training plan to develop strategic thinking skill through programs like critical thinking and problem solving technique, thinking and acting like an entrepreneur etc. Increase audience engagement and knowledge by dispensing information using Training Program To Develop Strategic Thinking Professional Development Training. This template helps you present information on eight stages. You can also present information on Critical Thinking, Problem Solving, Thinking And Acting using this PPT design. This layout is completely editable so personaize it now to meet your audiences expectations.
The slide showcases training plan to develop strategic thinking skill through programs like critical thinking and problem solving technique, thinking and acting like an entrepreneur etc.
- Critical Thinking
- problem solving
- Thinking And Acting
Em out of the box thinking idea flat powerpoint design
We are proud to present our em out of the box thinking idea flat powerpoint design. Concept of out of the box thinking has been displayed in this power point template diagram. To show this concept we have used graphic of box. Use this PPT diagram for business and marketing related presentations.
Cement their faith with our Em Out Of The Box Thinking Idea Flat Powerpoint Design. They will develop genuine belief.
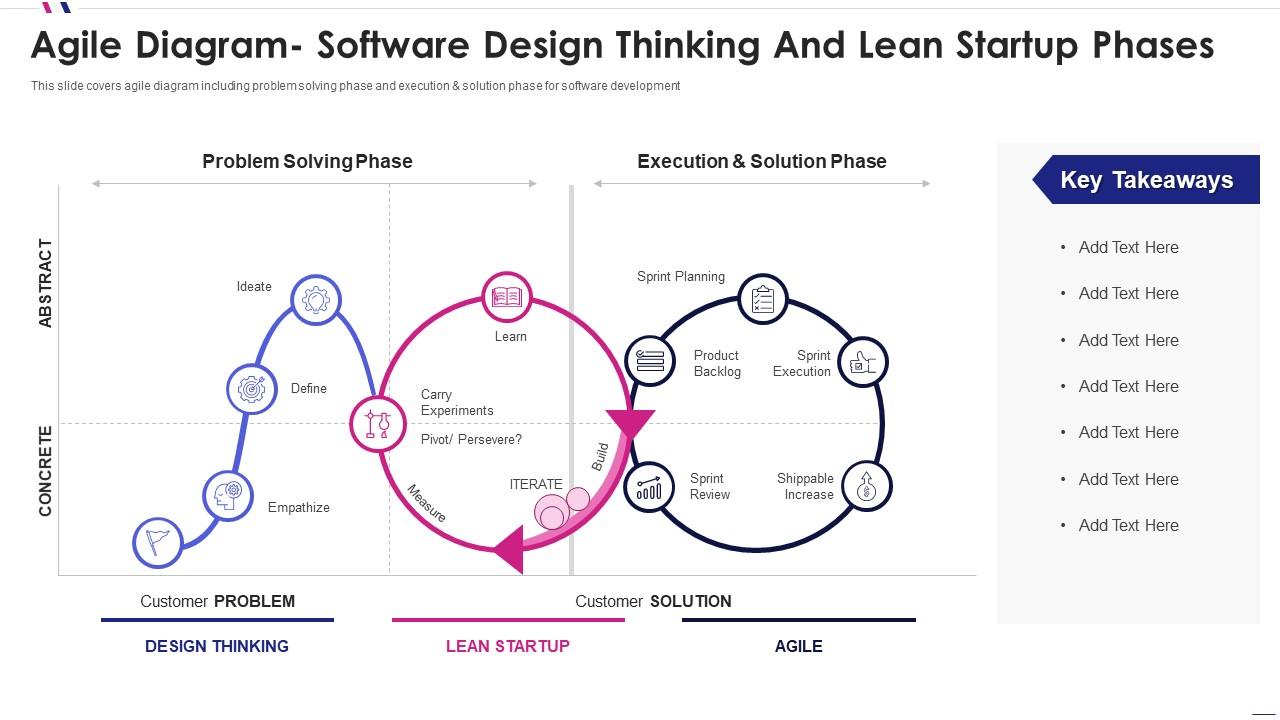
Agile software development diagram software design thinking lean startup phases
This slide covers agile diagram including problem solving phase and execution and solution phase for software development Present the topic in a bit more detail with this Agile Software Development Diagram Software Design Thinking Lean Startup Phases. Use it as a tool for discussion and navigation on Software, Execution, Solution. This template is free to edit as deemed fit for your organization. Therefore download it now.
This slide covers agile diagram including problem solving phase and execution and solution phase for software development

Home PowerPoint Templates Design Thinking
Design Thinking PowerPoint Templates & Presentation Slides
Design Thinking PowerPoint template by SlideModel includes Design Thinking presentation templates, Design Thinking slide designs, and Design Thinking PowerPoint backgrounds. Download and edit these templates for use in your presentations.
Featured Templates
Design Thinking Double Diamond for PowerPoint
Design Thinking Models PowerPoint Template

Design Thinking PowerPoint Templates
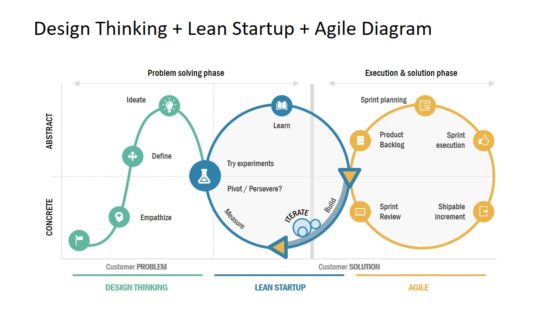
Design Thinking Lean Startup Agile Diagram for PowerPoint
Latest templates.
6-Step Head Diagram Morph Template for PowerPoint
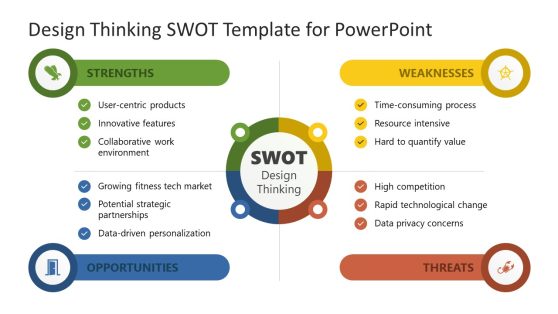
Design Thinking SWOT Template for PowerPoint
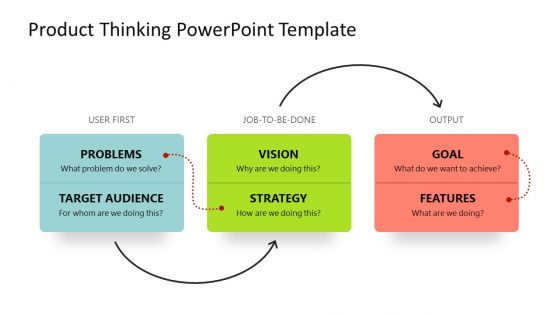
Product Thinking PowerPoint Template
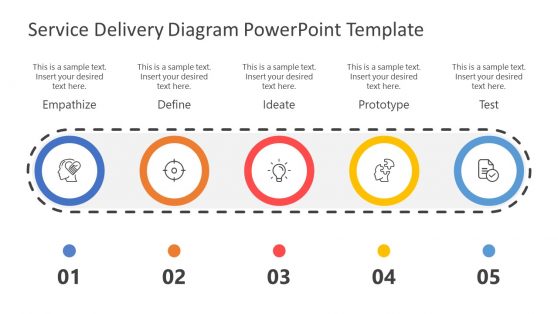
Service Delivery Process Diagram for PowerPoint
Blank Double Diamond PowerPoint Template
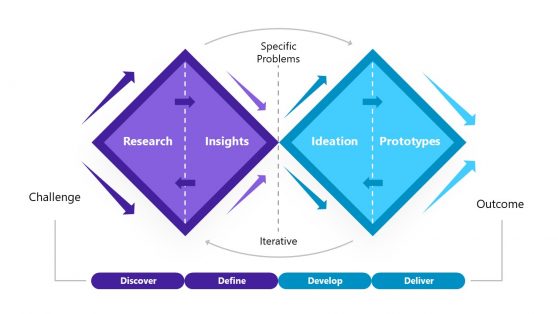
Double Diamond Model PowerPoint Template
Flat Value Proposition Canvas PowerPoint Template

Square Milestones PowerPoint Timeline Template
Gear Process Diagram PowerPoint Template
8 Steps Circular Nodes PowerPoint Diagram

Minimal Style Light Bulb Concept for PowerPoint

De Bono’s Six Thinking Hats PowerPoint Template
Design Thinking refers to a process in which professionals aim to understand the user, challenge prevalent assumptions, and redefine the problems in order to identify alternative solutions that may not have been visible in the initial levels of understanding.
What is Design Thinking?
Design Thinking process aims to find alternative solutions to various problems by having a deep understanding of the user, challenging the ongoing assumptions, and redefining problems. It is a solution-based approach for solving prevalent problems. It involves a hands-on approach for solving problems, as well as gives a different way of working and thinking.
Download Design Thinking PowerPoint presentation templates by SlideModel to present Design Thinking of a particular problem in your organization.
What is a Design Thinking PowerPoint presentation template?
A Design Thinking PowerPoint presentation template is a presentation template that users can use to demonstrate the design thinking they have used, present a design thinking process or analysis to an audience, or can use in a particular project.
These templates include various illustrative slide designs, PowerPoint backgrounds, and Design Thinking presentation templates that users can download and edit according to their need.
How can a Design Thinking PowerPoint presentation template be used in a presentation?
A Design Thinking PowerPoint presentation template can be used in a presentation by downloading and editing the template in PowerPoint, Google Slides, or Keynote.
Each template comes with a description and the details about the number of slides, the colors, and the supported versions. Edit the text, colors, and size of the templates to customize it according to your preference.
Download Unlimited Content
Our annual unlimited plan let you download unlimited content from slidemodel. save hours of manual work and use awesome slide designs in your next presentation..

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Oct 1, 2019 · Design thinking is an iterative process that involves empathizing with users, defining problems from their perspective, ideating solutions, prototyping ideas, and testing prototypes with users. It focuses on understanding user needs through observation and interviews to identify root problems.
These PPT templates facilitate the visualization of complex concepts, making it easier to convey the five stages of Design Thinking: Empathize, Define, Ideate, Prototype, and Test.In the Empathize stage, presenters can use slides to showcase user research findings, personas, and empathy maps, allowing the audience to grasp the users' perspectives.
Design Thinking Process PPT Slide. Start your presentation by explaining what Design Thinking is. You will find a circular diagram to display the five steps of the Design Thinking process: empathize, define, ideate, prototype, and test. This section will give your audience an overview of how the whole process looks like.
Download the All About Design Thinking presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides and start impressing your audience with a creative and original design. Slidesgo templates like this one here offer the possibility to convey a concept, idea or topic in a clear, concise and visual way, by using different graphic resources.
Implementing Design Thinking Powerpoint Ppt Template Bundles. Introduce your topic and host expert discussion sessions with this Implementing Design Thinking Powerpoint Ppt Template Bundles. This template is designed using high-quality visuals, images, graphics, etc, that can be used to showcase your expertise.
A Design Thinking PowerPoint presentation template can be used in a presentation by downloading and editing the template in PowerPoint, Google Slides, or Keynote. Each template comes with a description and the details about the number of slides, the colors, and the supported versions.