

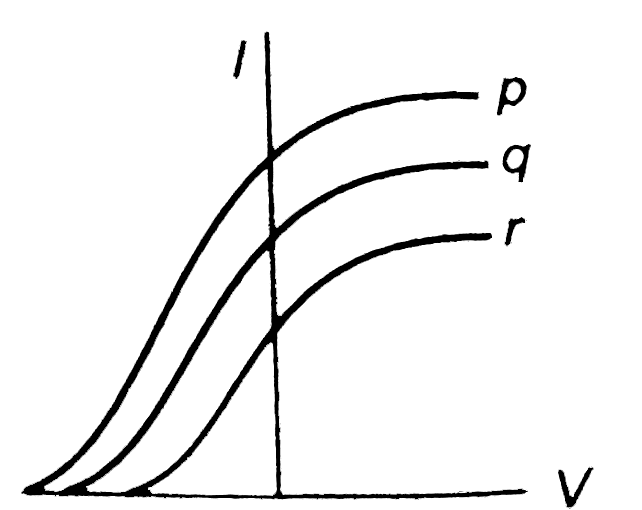
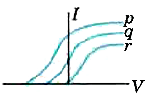
Photoelectric effect experiments are performed using three different metal plates p, q and r having work functions Φ p = 2.0 e V , Φ q = 2.5 e V a n d Φ r = 3.0 e V respectively. A light beam containing wavelengths of 550 nm, 450nm and 350nm with equal intensities illuminates each of the plates. The correct I - V graph for the experiment is : [Take hc = 1240 eV nm]

The correct option is B intensity is same for all the wavelengths, hence current would remain same.The difference between the energy of photon and work function is proportional to the stopping potential.the difference would be greatest for p plate . Watch the next video for the solution.

Photoelectric effect experiments are performed using three different metal plates p,q and r having work functions ϕ p = 2.0 e V , ϕ q = 2.5 e V a n d ϕ r = 3.0 e V , respectively. A light beam containing wavelengths of 550 nm, 450 nm and 350 nm with equal intensties illuminates each of the plates. The correct I-V graph for the experiment is (IIT-JEE-2009)
A student performs an experiment to observe photoelectric effect by shining light on a metal surface. The light source limits light of wavelength 450nm. The table given below lists the available metals and their corresponding work functions M e t a l ϕ ( e v ) T u n g s t e n 4.5 L i t h i u m 2.3 B a r i u m 2.5 T a n t a l u m 4.2
Suppose the photoelectric experiment is done separately with these metals with light of wavelength 450nm. The maximum magnitude of stopping potential amongst all the metals is

Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
Photoelectric effect experiments are performed using three different metal plates p, q and r having work function ${{\phi }_{P}}=2eV$, ${{\phi }_{q}}=2.5eV$ and ${{\phi }_{r}}=3eV$ respectively. A light beam containing wavelengths of 550nm, 450nm, and 350nm with equal intensities illuminates each of the plates. The correct I – V graph for the experiment is: (Take hc = 1240 eVnm) A. B. C. D.
- Question Answer
- Photoelectric effect experimen...

Repeaters Course for NEET 2022 - 23
- High School
- You don't have any recent items yet.
- You don't have any courses yet.
- You don't have any books yet.
- You don't have any Studylists yet.
- Information
Lab Report 5 - Experiment 6: The Photoelectric Effect
Classical physics (ph102), the university of the south pacific.
Students also viewed
- PH102 Exam (2018 ) - test papers
- PH102 Exam (2016 ) - test papers
- PH102 Exam (2019 ) - test papers
- PH102 Exam (2022) - test papers
- PH102 Final Exam (2023)
- PH102 Exam (2017 ) - test papers
Related documents
- PH102 short test 2 - 2019
- Test 1 Solutions 2022 - test papers
- PH 102 lab 4 final - Lab
- Determination OF THE Ratio OF THE Specific Heats OF AIR
- Lab Report 4 - Experiment 12: The Series Resonant Circuit
- Lab write up 4 ph 102
Related Studylists
Preview text, ph103 – quantum & electrical physics, experiment 6: the photoelectric effect.
This experiment aims for the following [ CITATION Kum13 \l 3081 ];
To examine some aspects of the photoelectric effect. also, to determine the Planck’s constant value denoted as ‘h’.
The following list below are the electronic components required to conduct the experiment [CITATION Kum13 \l 3081 ];
IEC Photoelectric Unit which comprises a photo emissive cell,
a high gain transistor amplifier,, a calibrated voltage divider,, a dry battery of 9v,, the cro unit and the color filters, and a tungsten filament lamp of 40w..
IEC Photoelectric Unit
Results Data Analysis:
There are three parts carried out in this experiment. The first part is called the Photo-electric Effect which it explains the effect of photo electric for the backing voltage and the tube current. The second part is called Planck’s Constant, h where it explains the purpose of backing voltage increasing until the tube current gives zero and it also will tabulate the data table provided in the manual together with graphs, calculation and comparison. And the third and last part is called relationship between Illumination and Current where it shows a data table together with a graph and observational reasons regarding the phototube current.
Part A: Photo Electric Effect
The photoelectric effect for the backing voltage was recorded as 0Volts whereas the tube current observed to be oμA. The reading of the tube current happens or occur the moment the light is connected to the rails of the tube. Hence, 0μA is the amount of current that has been passed due to the electrons being omitted from the metal surface in the photoelectric unit
Part B: Planck’s Constant (h)
What is the purpose of doing this? Step 3
The following table presented the measured and calculated data of all values needed for this particular part and will also be used to sketch the graph of backing voltage against frequency, obtaining the Planck constant and its percentage error. Also, below (above the table) is the sample calculation of the frequency and the average backing voltage in which filter color orange is used. Note that the speed of light, c is 3 × 108 m / s whereas λ is wavelength which is given in the table below.
Sample calculation of Frequency & Backing Voltage:
Frequency (Orange), f = cλ = 3 × 10
8 530 × 10 − 9 =5 × 10
Average backing voltage (Orange),
V =| T 1 + T 32 + T 3 |=|(−0)+(−0 3 )+(−0)|=0.
-2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
f(x) = 0 x − 1.

Backing Voltage Vs Frequency
Frequency ((×10^14 ) 𝐀𝐀
Backing Voltage (V)
0 5 5 6 6 7 7.
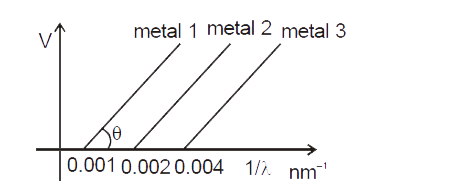
According to the theory behind photoelectric effect, we know that the electro-voltage, eV is equal to the product of planck’s constant, h and frequency, f subtracting the work function,
φ. And when the electro-voltage, eV equation compares to the quadratic equation, there are some comparisons which can be determined and one is that the slope of the graph of backing voltage versus frequency is equals to the product of planck’s constant and frequency in electro-volts. Another comparison is that the work function, is equals to the y-interceptɸ of the graph. The equation of the trend line of the graph above is approximately equals to
0 – 1. All the details expressions are shown below. Note that f = cλ .
eV = hf − φ≅y = mx + c
V = hceλ − φe = hce 1 λ − φe,so the slope , m = hce →h = m ×ec ∧ y −∫. = φe
¿ the graphabove ,the trend lineequationis y =0 x −1.
thereforem =0∧ y −∫. =1.
So, the planck’s constant determine from the graph above is 1 × 10 − 28 J ∨1917866 × 10 − 34 J whereas the accepted planck’s constant value is 6 × 10 − 34 J . And that makes a difference of around 1 × 10 − 26 %=0 ... 001918 % ≈ 0 %. Hence, in comparison of the two planck’s constant value, there are not much difference which shows a bit of accuracy while measuring the trials of backing voltage. Thus, the percentage error of planck’s constant is approximately 0%.
Part C: Relationship between Illumination and Current
The data table given below records the dimension of apertures of different size which will also be used to determine the area of each aperture size and also the phototube current. Note that the area of the aperture is determined using the given diameter.
Diameter (m) Area ( × 10 − 3 m 2 ) Phototube Current (μA) 0 0 0. 0 0 0. 0 0 0. 0 1 0.
All characteristics of light described by quantum theory and according to the experimental analysis above, the data shows the release of light energy from the energy source packs of the frequency specifically due to the emission of electrons from the metal surface. And in comparison, to Einstein’s theory which states that light travels in a group of energy where each energy group called photon and all individual photons has the same amount of energy quantity as the product of frequency and planck’s constant. The graph of backing voltage against the frequency showcases a clear image of quantum nature theory of light.
The backing voltage depends on the light frequency due to the relationship expressed in the formula of electric-voltage eV = hf − φ where hf is the energy source and work function ɸ is minimum energy of metal. A clear image displaying the relationship is shown in the graph of backing voltage against frequency above. However, there is no relationship between the backing voltage and intensity but the frequency of light does have a relationship with intensity. Hence, light frequency is directly proportional to both backing volts and intensity.
The photoelectric effect can be observed in other metal surfaces with the equivalent incident light condition depending on the type of the metal. However, it is not necessary because all metals have its’ own work function in which the minimum energy needed to free electrons from its surface. For instance, metals with a low work function such as potassium can display photoelectric the moment it is illuminated by lower energy photons. On the other hand, metals with higher work function needs more active photons.
Conclusion:
To conclude, the experiment was successfully completed where all the required tables, graphs and calculations were all displayed above. The photoelectric effect was able to be observed from the first part of the experiment due to the backing voltage of 0V and tube current of 0μA. In the second part, the planck’s constant of 1 × 10 − 28 J was able to determine from the graph of stopping or backing voltage versus frequency and in comparison, with the accepted value of the backing voltage of 6 × 10 − 34 J , the percentage error is approximately 0%. And in the third part, the relationship of the current and illumination was able to be observed from the graph of phototube current versus aperture area. Thus, there are certain experimental errors occur during the process of the
experiment, these errors happen due to old electrical components and the lack of accuracy in data readings.
References:
Kumar, D. S. et al., 2009. PH103: Quantum & Electrical Physics, Suva: Physics Department.
- Multiple Choice
Course : classical physics (ph102)
University : the university of the south pacific.

- Discover more from: classical physics ph102 The University of the South Pacific 86 Documents Go to course
- More from: classical physics ph102 The University of the South Pacific 86 Documents Go to course
- More from: Studocu by Sean Bourne 13 13 documents Go to Studylist
- Bihar Board
- Online Class
- Ask Doubt on Whatsapp
- Search Doubtnut
Photoelectric effect experiments are performed using three different metal plates p , q and r having work function ϕ p = 2.0 e V , ϕ e = 2.5 e V and ϕ r = 3.0 e V respectively A light beam containing wavelength of 550 n m , 450 n m and 350 n m with equal intensities illuminates each of the plates . The correct I - V graph for the experiment is [Take hc = 1240 eV nm]
none of these
More from this Exercise

The correct Answer is: D
K p = e p - ϕ p = 1240 550 - 2.0 = 0.2545 e v k q = e q - ϕ q = 1240 50 - 2.5 = 0.255 e v k r = e r - ϕ r = 1240 350 - 3.0 = 0.543 e v in the above equation, k represents maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons annd e, the energy of incident right. from the above values we can see that stopping potential. | v r | > | v q | > | v p | further, their intensities are equal, but energy of individual photon of r is maximum. hence, number of photons incident (per unit area per unit time) of r can be assumed to be least. hence, saturation currennt of r should be minimu. keeping these points in mid no option seems to be correct. the correct graph is shown below, ., topper's solved these questions, similar questions.
Find the threshold wavelengths for photoelectric effect from a copper surface, a sodium surface and a cesium surface. The work functions of these metals are 4.5 e V, 2.3 eV and 1.9 eV respectively.
Three photo diodes D 1 D 2 and D 3 are made of semiconductors having band gaps of 2.5 eV, 2 eV and 3 eV respectively. Which of them will not be able to detect light of wavelength 600 nm ?
Knowledge Check
Photoelectric affect experiments are performer using ther different medal plates p , q and r having work function phi_(p) = 2.0 ev, phi_(e) = 2.5 ev and phi_(r) = 3.0 ev r e s p e c t i v e l y a l i g h t b e a m c o n t a ∈ ∈ g w a v e ≤ n > h o f 550nm , 450 nm and 350nm w i t h e q u a l ∫ e n s i t i e s i l l u min a t e s e a c h o f t h e p l a t e . t h e c or r e c t 1 -v g r a p h f or t h e exp e r i m e n t i s [take hc = 1240 ev nm].
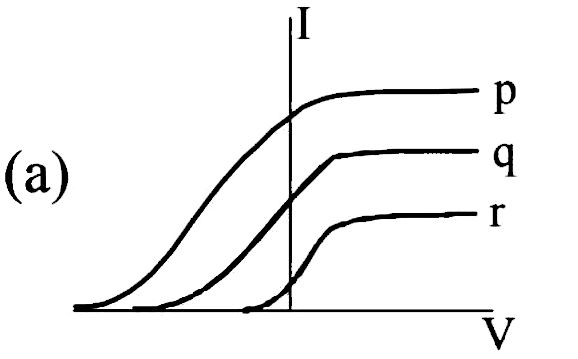
Photoelectric effect experiments are performed using three different metal plates p,q and r having work functions ϕ p = 2.0 e V , and phi_q=2.5eV and phi_(tau) = 3 e V and wavelengths of 550 nm,550nm, and 350 nm with equal intensities , illuminates each of the plates . The correct I - V graph for the experiment is (Take hc = 1240 eV nm)
Three metals A B and C have work functions as 15.5eV, 24eV and 30.5 eV respectively. If the light of wavelength 500 Å is incident of each metal, which of the following is correct?
Three photo diodes D 1 , D 2 and D 3 are made of semiconductors having band gaps of 2.5 eV, 2eV and 3eV respectively. Which of them will not be able to detect light of wavelength 600 nm?
(a) In a photoelectric experiment, the collector plate is at 2.0 V with respect to the emitter plate made of copper ( ϕ = 4.5 e V ) . The emitter is illuminated by a source of monochromatic light of wavelength 200 nm. Find minimum and maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons reaching the collector. (b) A small piece of cesium metal ( ϕ = 1.9 e V ) is kept a distance of 20 cm from a large metal plate having a charge density of 8.85 × 10 − 9 C / m 2 on the surface facing the cesium piece. A monochromatic light of wavelength 400 nm is incident on the cesium piece. Find minimum and the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons reaching the large metal plate. Neglect any change in the electric field due to the presence of small piece of cesium.
The photons from the balmer series in Hydrogen spectrum having wavelength between 450 n m to 700 n m are incident on a metal surface of work function 2 e V find the maximum kinetic energy os ejected electron (Given hc = 1242 eV nm)
Light of wavelength 350 nm falls on a metal having work function of 2eV. What is maximum possible magnitude of linear momentum of ejected electron ?
MHTCET PREVIOUS YEAR PAPERS AND PRACTICE PAPERS - ELECTRONS AND PROTONS - Exercise 2
The act of photoelectric effect taking place with a certain photosensi...
A point source of light is used in a photoelectric effect. If the sour...
If the frequency of light in a photoelectric experiment is doubled the...
The cathode of a photoelectric cell is changed such that the work func...
In a photoelectric experiment, the potential difference V that must be...
what should be the velocity of an electron so that its momentum becom...
From the figure describing photoelectric effect we may infer correctly...
Cathode rays enter a magnetic field makin oblique angle withh the line...
The work function for aluminium is 4.125 eV. The cut-off wavelength fo...
According to Einstein's photoelectric equation, the plot of the maximu...
Photon and electron are given same energy (10^(-20) J). Wavelength ass...
Match column I (fundamental experiment) with column II (its conclusion...
When a certain metallic surface is illuminated with monochromatic ligh...
Which of the following figure represents the variation of particle mom...
Threshold wavelength for lithium metal is 6250 Å. For photo emission, ...
In a photoelectric experiment the relation between applied potential d...
Photoelectric effect experiments are performed using three different m...
Light of two different frequencies whose photons have energies 1eV and...
Light of intensity 10^(-5)Wm^(-2) falls on a sodium photocell of surfa...
Work function for caesium metal is 2.14 eV. Let a beam of light of fre...

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Photoelectric effect experiments are performed using three different metal plates `p,q` and`r` having work function `phi_(p) = 2.0 eV, phi_(e) = 2.5 eV and phi_(r) = 3.0 eV` respectively A light beam containing wavelength of `550nm , 450 nm` and `350nm ` with equal intensities illuminates each of the plates .
Photoelectric effect experiment are performed using three different metal plates (x, y, z) having work function equal to 2.0 eV, 2.5 eV and 3.0 eV, respectively. A light beam, containing wave length of 550 nm, 450 nm and 350 nm, having equal intensity of illumination, is incident on each of the three plates. ...
Photoelectric effect experiments are performed using three different metal plates p, q and r having work functions Φ p = 2.0 e V, Φ q = 2.5 e V a n d Φ r = 3.0 e V respectively. A light beam containing wavelengths of 550 nm, 450nm and 350nm with equal intensities illuminates each of the plates. The correct I - V graph for the experiment is ...
Photoelectric effect experiments are performed using three different metal plates p, q and r having work function ${{\phi }_{P}}=2eV$, ${{\phi }_{q}}=2.5eV$ and ${{\phi }_{r}}=3eV$ respectively. A light beam containing wavelengths of 550nm, 450nm, and 350nm with equal intensities illuminates each of the plates.
The photoelectric effect was able to be observed from the first part of the experiment due to the backing voltage of 0V and tube current of 0μA. In the second part, the planck's constant of 1 × 10 − 28 J was able to determine from the graph of stopping or backing voltage versus frequency and in comparison, with the accepted value of the ...
2. Place a filter in front of the photoelectric cell. 3. Keeping the voltage constant and position of photocell fixed, increase the distance of lamp from photo-cell in small steps. In case note the position of the lamp r on the optical bench and the current I. 4. The experiment may be repeated with other filters (at least 2 filters). µA aA C ...
18. The Photo-Electric Effect¶ 18.1. Background¶. The experiment serves to demonstrate the photoelectric effect, for which Einstein was awarded a Nobel prize, and in the process determine Planck's constant, \(h\). The photoelectric effect is the process whereby a photon of energy \(E=h\nu\), incident on the surface of a conductor, transfers its energy to one of the electrons of an atom.
Photoelectric effect experiments are performed using three different metal plates p,q and r having work functions ϕ p = 2.0 e V, and phi_q=2.5eV and phi_(tau) = 3 e V and wavelengths of 550 nm,550nm, and 350 nm with equal intensities , illuminates each of the plates . The correct I - V graph for the experiment is (Take hc = 1240 eV nm)
Photoelectric effect experiments are performed using three different metal plates p, q and r having work functions ϕ_p=2.0 eV, ϕ_q=2.5 eV and ϕ_r=3.0 eV, res...
few atoms, photons and/or electrons does one need to use Quantum M echanics. * Experimental Apparatus The photoelectric effect in this ex-periment occurs at the cathode of an IP39 phototube. The phototube is constructed as shown in Figure 2. The IP39 phototube is designed to function as a diode where light, inci-dent on the tube, illuminates the