How to Write an Operations Plan Section of your Business Plan
Free Operations Plan Template
- June 26, 2024

An operational plan bridges the gap between high ambitions and actual achievements. This essential integral section helps businesses thrive, achieve their goals, and handle challenges with accuracy and purpose.
But is it challenging for you to write one in a manner that shows a clear picture of your business operations? Drafting the operations plan section can be tricky due to the uncertainties of the business environment and the risks associated with it.
Well, worry not you’re at the right place! Here, we will see how to write an engaging operational plan in a business plan with an example. So let’s get going.

What is an operations plan?
An operations plan of a business plan is an in-depth description of your daily business activities centered on achieving the goals and objectives described in the previous sections of the plan. It outlines various departments’ processes, activities, responsibilities, and execution time frame.
The operations section explains in detail the role of a team or department in the collective accomplishment of your goals. In other words, it’s a strategic allocation of physical, financial, and human resources toward reaching milestones within a specific timeframe.
Key questions your operational plan should address

A successful operational plan section of your business plan should be able to answer the following questions:
- Who is responsible for a specific task or department?
- What are the tasks that need to be completed?
- Where will these operations take place?
- When should the tasks be completed? What are the deadlines?
- How will the tasks be performed? Is there a standard procedure?
- How much is it going to cost to complete these tasks?
Let’s see how to write the operations section that answers all the above questions:
Create winning business plans with our
AI Business Plan Generator
Plans starting from $7/month

How do you write an operations plan section?
Writing an operations plan within a business plan involves summarizing the day-to-day tasks necessary to run the business efficiently and meet its goals in both the development and manufacturing phases of the business.
Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Development phase
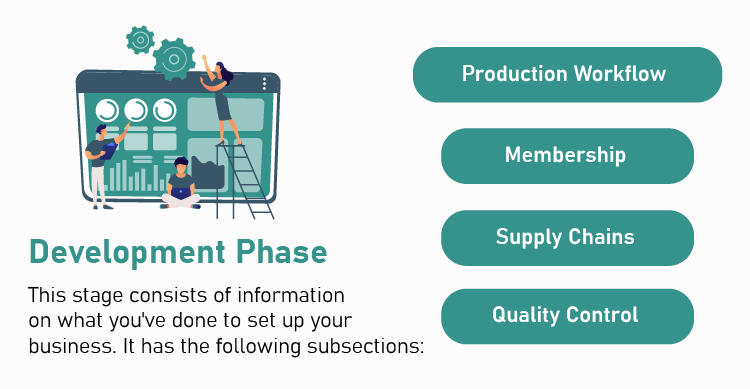
In this stage, you mention what you’ve done to get your business operations up and running. Explain what you aim to change and improvise in the process. These are the elements your development section will contain:
Production workflow
Explain all the steps involved in creating your product. Provide a detailed description of each step, including any inefficiencies and the actions needed to address them. Here, you also mention any inefficiencies that exist and talk about the actions that need to be taken to tackle them.
Write down the risks involved in the production and potential problems you may face later down the line. State the safety measures employees take to avoid any misfortune while working. Explain how you store hazardous material and discard waste.
Mention any industry organizations and associations you’re a part of or plan to join. It’s essential to include this information to convey to the reader that you’re aware of the organizations and associations in your industry.
Supply chains
Here, you mention the vendors you work with to sell your products. Give a quick rundown of the agreements you signed with them. Mention the terms and conditions, prices, and timeframe of the contract. You can also mention if you have any backup suppliers if the existing ones fail to fulfill the requirements.
Quality control
Describe the measures you’re taking to assure and verify the quality of the end product. If you’re working towards getting a product certification, explain the steps you take to meet the set standards.
2. Manufacturing phase
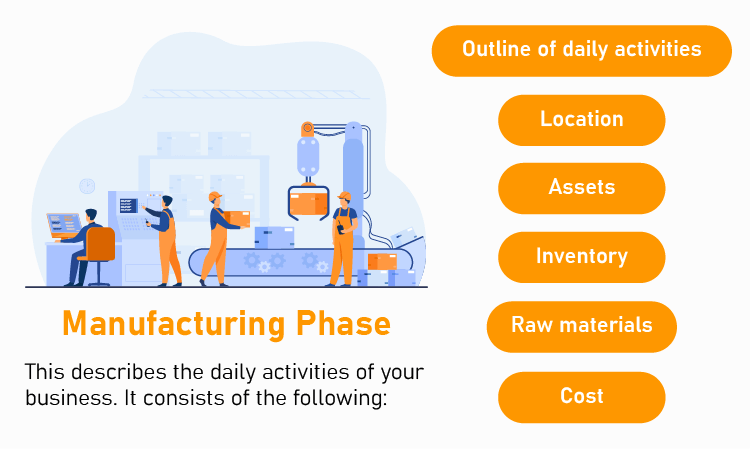
The development stage acquaints the reader with the functioning of your business, while the manufacturing stage describes the day-to-day operation. This includes the following elements:
Outline of daily activities
Create an outline of the day-to-day activities of the production process. This includes the hours of operation, days the business will be open, and whether the business is seasonal or not.
Mention the location of your business , other branches you have, and their locations. If available, include images or drawings of the buildings, lease documents, real estate agreements, and other relevant documents. If you include these in your plan, mention why they’re crucial.
Tools and equipment
Describe the tools and machinery you use. You should also include the cost of the equipment; these will be important to predict financial requirements.
List down all your assets. These include land, buildings, tools, machinery, vehicles, and furniture. Include a legal description and the value of these assets.
Special requirements
If you require any additional facilities like water supply or power requirements, you mention them here. Specify what you need to do or have already done to acquire permissions for these requirements.
Raw materials
Mention your raw material suppliers. If you need any extra materials, you can also include them in your operations plan. Here, you also mention the contracts and agreements with your suppliers.
Productions
Explain the production process and the time required to produce one unit. Include the factors that may disrupt the production flow. Further, mention your strategies to tackle these inefficiencies to avoid delays in manufacturing.
Here, you state the process of storing manufactured products, managing the stock, and the costs of the storage spaces. Stringent management of inventory is essential to maintain product quality and assure customer satisfaction.
Feasibility
To ensure the viability and effectiveness of your product, detail any tests it has undergone. This includes prototype testing to evaluate the design and functionality.
Additionally, highlight product or service testing, such as performance, safety, and user experience assessments. These tests validate your product’s readiness for the market, ensuring it meets customers’ needs and regulatory standards.
Include the pricing strategy for your products or services. You can also include the final prices of your products.
Outline your pricing strategy including which approach you used, for example—cost-plus, value-based, or competitive pricing. Include the final prices of your products or services, providing a breakdown if there are different tiers or packages.
Why do you need an operations plan?
An operations plan is like an instruction manual for your business. It helps investors assess your credibility and understand the structure of your operations.
Internally, an operations plan works as a guide, which helps your employees and managers to know their responsibilities. It also helps them understand how to execute their tasks in the desired manner—all while keeping account of deadlines.
The operations plan helps identify and cut the variances between planned & actual performance and makes necessary changes.
It helps you visualize how your operations affect revenue and gives you an idea of when you need to implement new strategies to maximize profits. Some of the advantages of preparing an operations plan include:
Offers clarity
Operational planning makes sure that everyone in the audience and team is aware of the daily, weekly, and monthly work. It improves concentration and productivity.
Contains a roadmap
Operational planning makes it much easier to reach long-term objectives. When members have a clear business strategy to follow—productivity rises, and accountability is maintained.
Set a benchmark
It sets a clear goal for everyone about what is the destination of the company and how to reach it.
Manages resources
It supports you in allocating resources, such as human resources, equipment, and materials, ensuring that nothing is wasted and everything is used optimally.
Helps in decision making
An operations plan helps make smart decisions by showing how the business runs day-to-day. It provides details on resources, wise investments, and effective risk management, ensuring that decisions improve overall business operations.
Operations plan essentials
Now that you have understood the importance of the operations plan, let’s go through the essentials of an operations plan:
Strategic plan
Your operations plan is fundamentally a medium for implementing your strategic plan . Hence, it’s crucial to have a solid plan to write an effective operations plan.
Having clear goals is one of the most important things for an operations plan. For clear goals, you need to think SMART:
- Specific: Clearly define what employees should achieve
- Measurable: Quantify the goal to track progress
- Attainable: Set ambitious but achievable goals
- Timely: Provide a deadline
Different departments will have their objectives, all supporting the main goal. All these strategic objectives are flexible and should align with the company’s long-term goals.
Key performance indicators
It’s essential to choose the right Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). It’s a good practice to involve all your teams while you decide your KPIs. Some of the important KPIs can be revenue growth, customer acquisition cost (CAC), net profit margin, churn rate, etc.
Creating a timeline with milestones is necessary for any business. It keeps everyone focused and helps track efficiency. If some milestones aren’t met in a certain period, then it’s time to re-evaluate them.
Examples of some milestones are:
- Hiring key team members in six months
- Setting checkpoints for different production phases like design, prototype, development, testing, etc.
- Acquiring the first 50 clients in a year
Now you’re all set to write an operations plan section for your business plan. To give you a headstart, we have created an operations plan example.
Operations Plan Example
We know this guide has been helpful for you in drafting a comprehensive operational plan section for your business plan.
If you’re still unsure or need help getting started, consider using business plan software like Upmetrics . It offers step-by-step guidance, so you won’t have to worry about what comes next.
Build your Business Plan Faster
with step-by-step Guidance & AI Assistance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a strategic plan and an operational plan.
A strategic plan outlines the long-term vision, mission, and goals of an organization, focusing on growth and direction over several years.
In contrast, an operational plan details the short-term tasks, processes, and resource allocation needed to achieve those strategic goals, emphasizing day-to-day efficiency and productivity.
What role does the operations plan play in securing funding for a business?
The operations plan defines the clear goals of your business and what actions will be taken daily to reach them. So, investors need to know where your business stands and it will prove the viability of the goals helping you in getting funded.
What are the factors affecting the operations plan?
Some of the factors that affect the operations plan are:
- The mission of the company
- Goals to be achieved
- Finance and resources your company will need
Can an operations plan be created for both start-up and established businesses?
Yes, both a startup and a small business need an operations plan to get a better idea of the roadmap they want for their business.
About the Author
Upmetrics Team
Upmetrics is the #1 business planning software that helps entrepreneurs and business owners create investment-ready business plans using AI. We regularly share business planning insights on our blog. Check out the Upmetrics blog for such interesting reads. Read more
Get started with Upmetrics Al
- 400+ sample business plans
- Al-powered financial planning
- Collaborative workspace
Reach Your Goals with Accurate Planning
- Contact sales
Start free trial
Operational Planning: How to Make an Operations Plan

The operations of your business can be defined as the sum of all the daily activities that you and your team execute to create products or services and engage with your customers, among other critical business functions. While organizing these moving parts might sound difficult, it can be easily done by writing a business operational plan. But before we learn how to make one, let’s first understand what’s the relationship between strategic and operational planning.
Operational Planning vs. Strategic Planning
Operational planning and strategic planning are complementary to each other. This is because strategic plans define the business strategy and the long-term goals for your organization, while operational plans define the steps required to achieve them.

Get your free
Operational Plan Template
Use this free Operational Plan Template for Word to manage your projects better.
What Is a Strategic Plan?
A strategic plan is a business document that describes the business goals of a company as well as the high-level actions that will be taken to achieve them over a time period of 1-3 years.
What Is an Operational Plan?
Operational plans map the daily, weekly or monthly business operations that’ll be executed by the department to complete the goals you’ve previously defined in your strategic plan. Operational plans go deeper into explaining your business operations as they explain roles and responsibilities, timelines and the scope of work.
Operational plans work best when an entire department buys in, assigning due dates for tasks, measuring goals for success, reporting on issues and collaborating effectively. They work even better when there’s a platform like ProjectManager , which facilitates communication across departments to ensure that the machine is running smoothly as each team reaches its benchmark. Get started with ProjectManager for free today.
What Is Operational Planning?
Operational planning is the process of turning strategic plans into action plans, which simply means breaking down high-level strategic goals and activities into smaller, actionable steps. The main goal of operational planning is to coordinate different departments and layers of management to ensure the whole organization works towards the same objective, which is achieving the goals set forth in the strategic plan .
How to Make an Operational Plan
There’s no single approach to follow when making an operation plan for your business. However, there’s one golden rule in operations management : your strategic and operational plans must be aligned. Based on that principle, here are seven steps to make an operational plan.
- Map business processes and workflows: What steps need to be taken at the operations level to accomplish long-term strategic goals?
- Set operational-level goals: Describe what operational-level goals contribute to the achievement of larger strategic goals.
- Determine the operational timeline: Is there any time frame for the achievement of the operational plan?
- Define your resource requirements: Estimate what resources are needed for the execution of the operational plan.
- Estimate the operational budget: Based on your resource requirements, estimate costs and define an operational budget.
- Set a hiring plan: Are there any skills gaps that need to be filled in your organization?
- Set key performance indicators: Define metrics and performance tracking procedures to measure your team’s performance.

Free Operational Plan Template
Leverage everything you’ve learned today with our template. This free operational plan template for Word will help you define your budget, timeline, KPIs and more. It’s the perfect first step in organizing and improving your operations. Download it today.
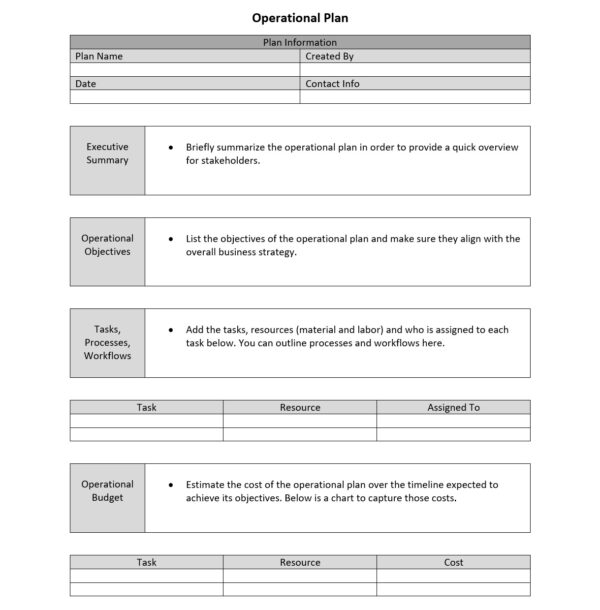
What Should be Included in an Operational Plan?
Your operational plan should describe your business operations as accurately as possible so that internal teams know how the company works and how they can help achieve the larger strategic objectives. Here’s a list of some of the key elements that you’ll need to consider when writing an operational plan.
Executive Summary
An executive summary is a brief document that summarizes the content of larger documents like business plans, strategic plans or operation plans. Their main purpose is to provide a quick overview for busy stakeholders.
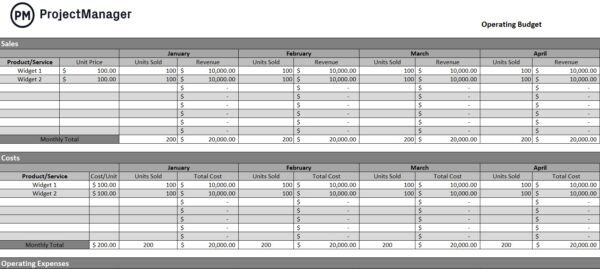
Operational Budget
An operational budget is an estimation of the expected operating costs and revenues for a given time period. As with other types of budget, the operational budget defines the amount of money that’s available to acquire raw materials, equipment or anything else that’s needed for business operations.
It’s important to limit your spending to stay below your operational budget, otherwise, your company could run out of resources to execute its normal activities. You can use our free operating budget template for Excel to track your operating costs.
Operational Objectives
It’s essential to align your operational objectives with your strategic objectives. For example, if one of your strategic objectives is to increase sales by 25 percent over the next three years, one possible operational objective would be to hire new sales employees. You should always grab your strategic plan objectives and turn them into one or multiple action items .
Processes & Workflows
Explain the various business processes, workflows and tasks that need to be executed to achieve your operational objectives. Make sure to explain what resources are needed, such as raw materials, equipment or human resources.
Operational Timeline
It’s important to establish a timeline for your operational plan. In most cases, your operational plan will have the same length as your strategic plan, but in some scenarios, you might create multiple operational plans for specific purposes. Not all operational plans are equal, so the length of your operational timeline will depend on the duration of your projects , workflows and processes.
Hiring Plan
Find any skills gap there might be in your team. You might need to hire a couple of individuals or even create new departments in order to execute your business processes .
Quality Assurance and Control
Most companies implement quality assurance and control procedures for a variety of reasons such as customer safety and regulatory compliance. In addition, quality assurance issues can cost your business millions, so establishing quality management protocols is a key step in operational planning.
Key Performance Indicators
It’s important to establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the productivity of your business operations. You can define as many KPIs as needed for all your business processes. For example, you can define KPIs for marketing, sales, product development and other key departments in your company. This can include product launch deadlines, number of manufactured goods, number of customer service cases closed, number of 5-star reviews received, number of customers acquired, revenue increased by a certain percentage and so on.
Risks, Assumptions and Constraints
Note any potential risks, assumptions and time or resource constraints that might affect your business operations.
What Are the Benefits of Operational Planning?
Every plan has a massive effect on all team members involved, and those can be to your company’s benefit or to their detriment. If it’s to their detriment, it’s best to find out as soon as possible so you can modify your operational plan and pivot with ease.
But that’s the whole point of operational planning: you get to see the effect of your operations on the business’s bottom line in real time, or at every benchmark, so you know exactly when to pivot. And with a plan that’s as custom to each department as an operational plan, you know exactly where things go wrong and why.
How ProjectManager Can Help with Operational Planning
Creating and implementing a high-quality operational plan is the best way to ensure that your organization starts out a project on the right foot. ProjectManager has award-winning project management tools to help you craft and execute such a plan.
Gantt charts are essential to create and monitor operational plans effectively. ProjectManager helps you access your Gantt chart online so you can add benchmarks for operational performance reviews. You can also create tasks along with dependencies to make the operation a surefire success.
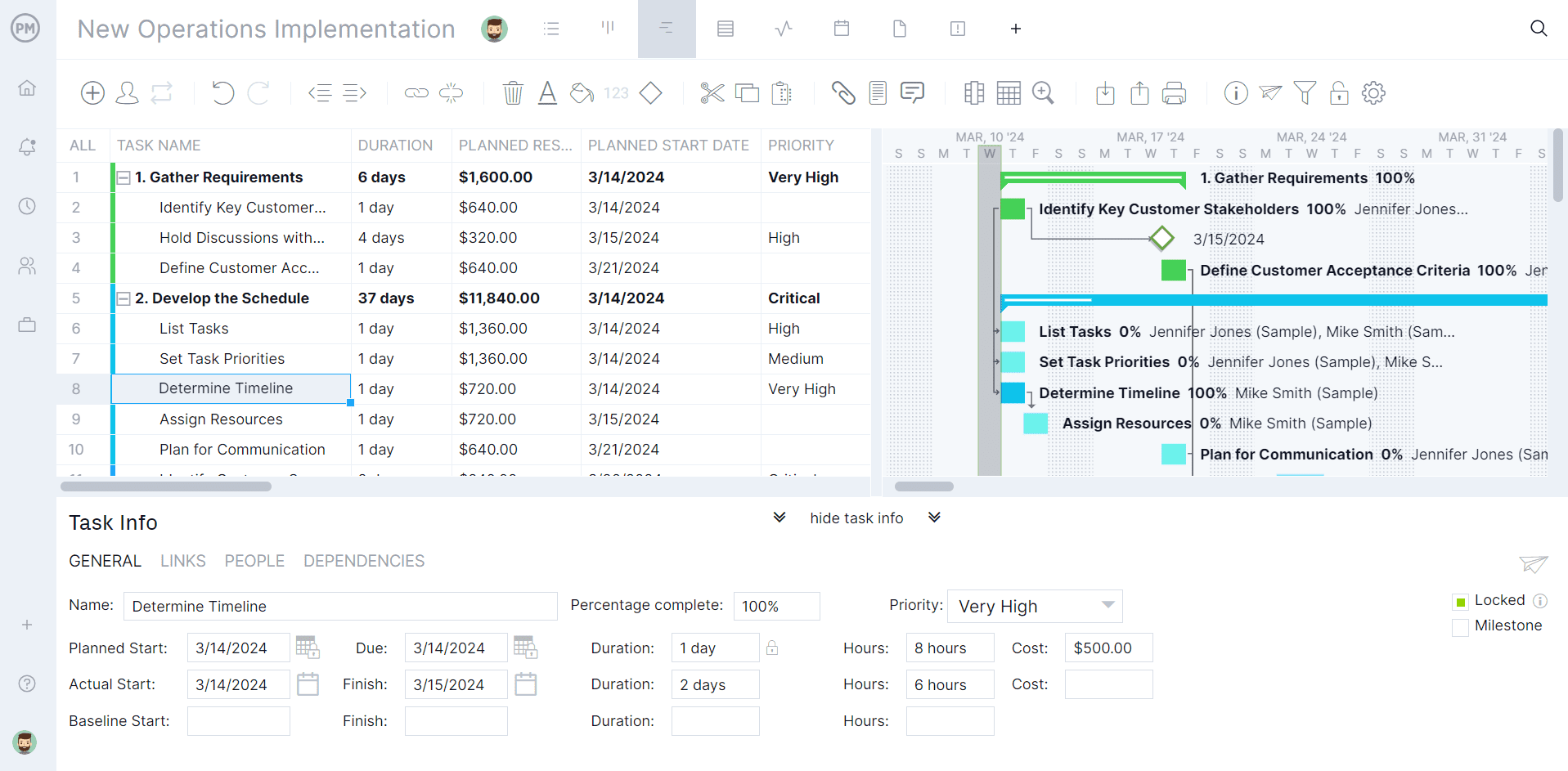
Whether you’re a team of IT system administrators, marketing experts, or engineers, ProjectManager includes robust planning and reporting tools. Plan in sprints, assign due dates, collaborate with team members and track everything with just the click of a button. Plus, we have numerous ready-made project reports that can be generated instantly, including status reports, variance reports, timesheet reports and more.
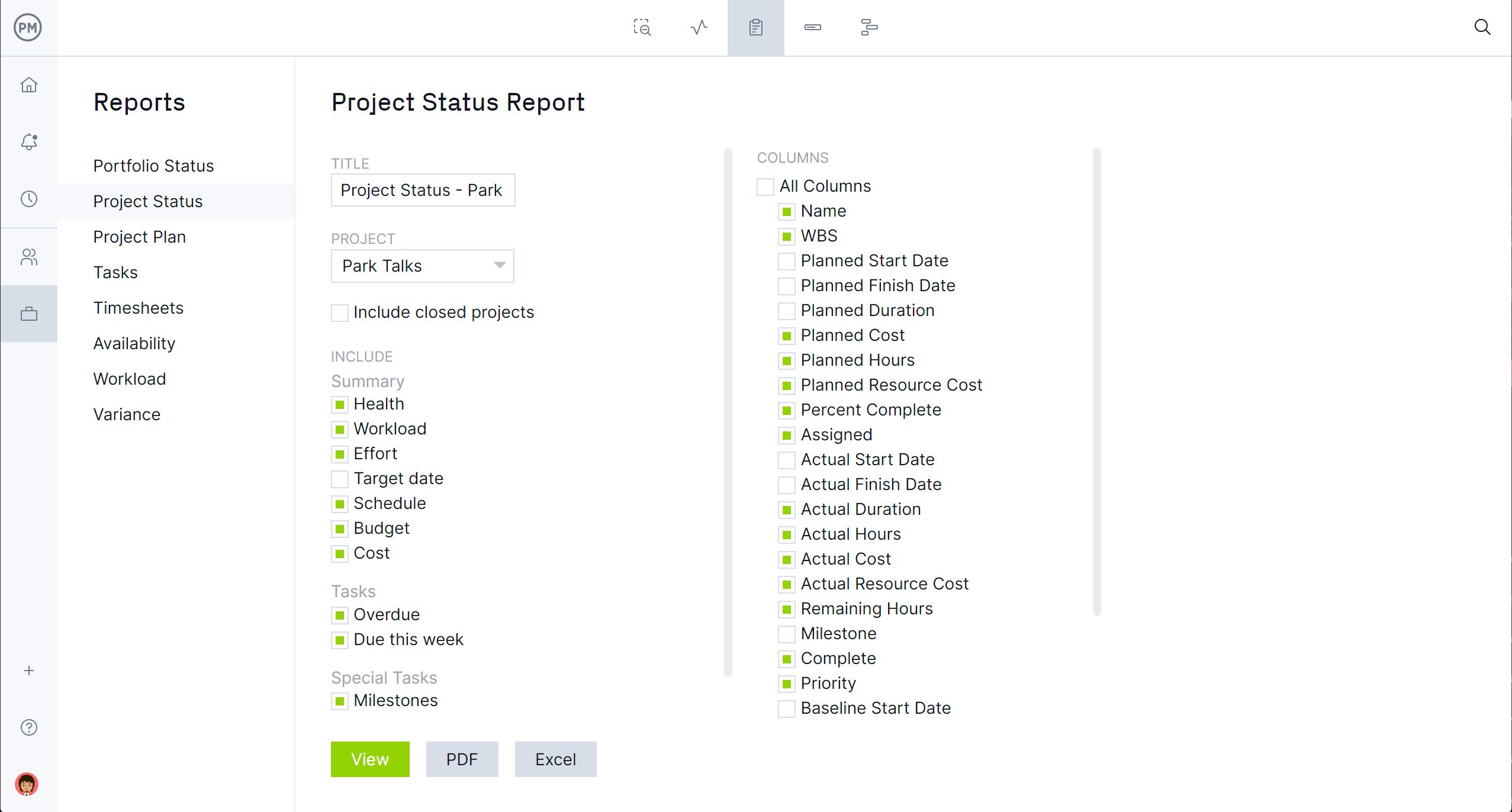
Related Operations Management Content
- Operational Strategy: A Quick Guide
- Operations Management: Key Functions, Roles and Skills
- Operational Efficiency: A Quick Guide
- Using Operational Excellence to Be More Productive
Operational planning isn’t done in a silo, and it doesn’t work without the full weight of the team backing it up. Ensure that your department is successful at each benchmark. ProjectManager is an award-winning pm software dedicated to helping businesses smooth out their operational plans for a better year ahead. Sign up for our free 30-day trial today.

Deliver your projects on time and on budget
Start planning your projects.
- Starting a Business
- Growing a Business
- Business News
- Science & Technology
- Money & Finance
- For Subscribers
- Write for Entrepreneur
- Tips White Papers
- Entrepreneur Store
- United States
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East
- United Kingdom
- South Africa
Copyright © 2024 Entrepreneur Media, LLC All rights reserved. Entrepreneur® and its related marks are registered trademarks of Entrepreneur Media LLC
Writing A Business Plan: Operations And Management
Feb 1, 1997
Generally, there are seven major components that make up a business plan. They are:
1. Executive summary
2. Business description
3. Market strategies
4. Competitive analysis
5. Design and development plans
6. Operations and management plans
7. Financial factors
The operations and management plan is designed to describe just how the business functions on a continuing basis. The operations plan will highlight the logistics of the organization such as the various responsibilities of the management team, the tasks assigned to each division within the company, and capital and expense requirements related to the operations of the business. In fact, within the operations plan you'll develop the next set of financial tables that will supply the foundation for the "Financial Components" section. The financial tables that you'll develop within the operations plan include:
*The operating expense table
*The capital requirements table
*The cost of goods table
There are two areas that need to be accounted for when planning the operations of your company. The first area is the organizational structure of the company, and the second is the expense and capital requirements associated with its operation.
Organizational Structure
The organizational structure of the company is an essential element within a business plan because it provides a basis from which to project operating expenses. This is critical to the formation of financial statements, which are heavily scrutinized by investors; therefore, the organizational structure has to be well-defined and based within a realistic framework given the parameters of the business.
Although every company will differ in its organizational structure, most can be divided into several broad areas that include:
*Marketing and sales (includes customer relations and service)
*Production (including quality assurance)
*Research and development
*Administration
These are very broad classifications and it is important to keep in mind that not every business can be divided in this manner. In fact, every business is different, and each one must be structured according to its own requirements and goals.
Terence P. McGarty in his book, Business Plans That Win Venture Capital , lists four stages for organizing a business:
1. Establish a list of the tasks using the broadest of classifications possible.
2. Organize these tasks into departments that produce an efficient line of communications between staff and management.
3. Determine the type of personnel required to perform each task.
4. Establish the function of each task and how it will relate to the generation of revenue within the company.
Once you have structured your business, however, you need to consider your overall goals and the number of personnel required to reach those goals.
In order to determine the number of employees you'll need to meet the goals you've set for your business, you'll need to apply the following equation to each department listed in your organizational structure:
In this equation, C represents the total number of customers, S represents the total number of customers that can be served by each employee, and P represents the personnel requirements. For instance, if the number of customers for first year sales is projected at 10,110 and one marketing employee is required for every 200 customers, you would need 51 employees within the marketing department.
10,110 ÷ 200 = 51
Once you calculate the number of employees that you'll need for your organization, you'll need to determine the labor expense. The factors that need to be considered when calculating labor expense (LE) are the personnel requirements (P) for each department multiplied by the employee salary level (SL). Therefore, the equation would be:
P × SL = LE
Using the marketing example from above, the labor expense for that department would be:
51 × $40,000 = $2,040,000
Once the organization's operations have been planned, the expenses associated with the operation of the business can be developed. These are usually referred to as overhead expenses. Overhead expenses refer to all non-labor expenses required to operate the business. Expenses can be divided into fixed -- those that must be paid, usually at the same rate, regardless of the volume of business -- and variable (or semivariable) -- those which change according to the amount of business.
Overhead expenses usually include the following:
*Maintenance and repair
*Equipment leases
*Advertising & promotion
*Packaging & shipping
*Payroll taxes and benefits
*Uncollectible receivables
*Professional services
*Loan payments
*Depreciation
In order to develop the overhead expenses for the expense table used in this portion of the business plan, you need to multiply the number of employees by the expenses associated with each employee. Therefore, if NE represents the number of employees and EE is the expense per employee, the following equation can be used to calculate the sum of each overhead (OH) expense:
OH = NE × EE
In addition to the expense table, you'll also need to develop a capital requirements table that depicts the amount of money necessary to purchase equipment you will use to establish and continue operations. It also illustrates the amount of depreciation your company will incur based on all equipment elements purchased with a lifetime of more than one year.
In order to generate the capital requirements table, you first have to establish the various elements within the business that will require capital investment. For service businesses, capital is usually tied to the various pieces of equipment used to service customers.
Capital for manufacturing companies, on the other hand, is based on the equipment required in order to produce the product. Manufacturing equipment usually falls into three categories: testing equipment, assembly equipment, and packaging equipment.
With these capital elements in mind, you need to determine the number of units or customers, in terms of sales, that each equipment item can adequately handle. This is important because capital requirements are a product of income, which is produced through unit sales. In order to meet sales projections, a business usually has to invest money to increase production or supply better service. In the business plan, capital requirements are tied to projected sales as illustrated in the revenue model shown earlier in this chapter.
For instance, if the capital equipment required is capable of handling the needs of 10,000 customers at an average sale of $10 each, that would be $100,000 in sales, at which point additional capital will be required in order to purchase more equipment should the company grow beyond this point. This leads us to another factor within the capital requirements equation, and that is equipment cost. If you multiply the cost of equipment by the number of customers it can support in terms of sales, it would result in the capital requirements for that particular equipment element. Therefore, you can use an equation in which capital requirements (CR) equals sales (S) divided by number of customers (NC) supported by each equipment element, multiplied by the average sale (AS), which is then multiplied by the capital cost (CC) of the equipment element. Given these parameters, your equation would look like the following:
CR = [(S &3247; NC) × AS] × CC
The capital requirements table is formed by adding all your equipment elements to generate the total new capital for that year. During the first year, total new capital is also the total capital required. For each successive year thereafter, total capital (TC) required is the sum of total new capital (NC) plus total capital (PC) from the previous year, less depreciation (D), once again, from the previous year. Therefore, your equation to arrive at total capital for each year portrayed in the capital requirements model would be:
TC = NC + PC - D
Keep in mind that depreciation is an expense that shows the decrease in value of the equipment throughout its effective lifetime. For many businesses, depreciation is based upon schedules that are tied to the lifetime of the equipment. Be careful when choosing the schedule that best fits your business. Depreciation is also the basis for a tax deduction as well as the flow of money for new capital. You may need to seek consultation from an expert in this area.
The last table that needs to be generated in the operations and management section of your business plan is the cost of goods table. This table is used only for businesses where the product is placed into inventory. For a retail or wholesale business, cost of goods sold , or cost of sales , refers to the purchase of products for resale -- the inventory. The products that are sold are logged into cost of goods as an expense of the sale, while those that aren't sold remain in inventory.
For a manufacturing firm, cost of goods is the cost incurred by the company to manufacture its product. This usually consists of three elements:
1. Material
3. Overhead
As in retail, the merchandise that is sold is expensed as a cost of goods, while merchandise that isn't sold is placed in inventory. Cost of goods has to be accounted for in the operations of a business. It is an important yardstick for measuring the firm's profitability for the cash-flow statement and income statement.
In the income statement, the last stage of the manufacturing process is the item expensed as cost of goods, but it is important to document the inventory still in various stages of the manufacturing process because it represents assets to the company. This is important to determining cash flow and to generating the balance sheet.
That is what the cost of goods table does. It is one of the most complicated tables you'll have to develop for your business plan, but it is an integral part of portraying the flow of inventory through your operations, the placement of assets within the company, and the rate at which your inventory turns.
In order to generate the cost of goods table, you need a little more information in addition to what your labor and material cost is per unit. You also need to know the total number of units sold for the year, the percentage of units which will be fully assembled, the percentage which will be partially assembled, and the percentage which will be in unassembled inventory. Much of these figures will depend on the capacity of your equipment as well as on the inventory control system you develop. Along with these factors, you also need to know at what stage the majority of labor is performed.
Part six of seven. Tomorrow, we'll cover the financial factors that go into your plan. Tips are updated daily at 8:30am PST or 11:30 EDT.
Want to be an Entrepreneur Leadership Network contributor? Apply now to join.
Editor's Pick Red Arrow
- Lock You Might Be Offending Your Co-Workers With These Passive-Aggressive Email Phrases — Here's What to Say Instead
- I Tried Buying a Car on Amazon. Here Are the Pros and Cons.
- 'I Just Hustled' : She Earned More Than $300,000 Wrapping Gifts Last Year — and It All Started With a Side Hustle
- Lock This One Act of Courage Completely Shifted My View on Leadership
- These Are the Top New and Emerging Franchises of 2024 — And You Can Start One for Less Than $5,000
- Lock More Than 75% of Americans Have Side Hustles During the Holidays — Here Are the Most Popular Gigs This Season
Most Popular Red Arrow
'wanted to cry for joy': mackenzie scott donates $65m gift to housing nonprofit.
It was Scott's second donation to the nonprofit and a complete surprise.
This Couple Wanted to Make an Everyday Household Product 'Unquestionably Better.' Now Their Business Sees Over $200 Million Annual Revenue: 'Obliterated Our Goals.'
Scott and Missy Tannen, co-founders of luxury bedding brand Boll & Branch, weren't impressed with the products on the market — so they created their own.
These Predatory Marketing Tactics Could Be Your Company's Biggest Threat
In a world where good technology quickly enables bad deeds, monitoring your brand identity and SEO safety needs to be as common as monitoring traffic, leads and conversions from your marketing programs.
Elon Musk Is Accusing OpenAI of 'Offering Vastly Inflated Compensation.' Here's How Much OpenAI Employees Really Make, From Technical to Communications Roles
Elon Musk accused OpenAI earlier this year of spending $1.5 billion on just 1,500 employees.
63 Small Business Ideas to Start in 2024
We put together a list of the best, most profitable small business ideas for entrepreneurs to pursue in 2024.
Klarna Is Replacing Workers With AI, but Claims Those Who Survived Cuts Will See Gains 'In Your Paycheck'
The "buy now, pay later" company stopped hiring new workers a year ago.
Successfully copied link
Need a consultation? Call now:
Talk to our experts:
- Strategic Planning
- E1 Treaty Trader Visa
- E2 Treaty Investor Visa
- Innovator Founder Visa
- UK Start-Up Visa
- UK Expansion Worker Visa
- Manitoba MPNP Visa
- Start-Up Visa
- Nova Scotia NSNP Visa
- British Columbia BC PNP Visa
- Self-Employed Visa
- OINP Entrepreneur Stream
- LMIA Owner Operator
- ICT Work Permit
- LMIA Mobility Program – C11 Entrepreneur
- USMCA (ex-NAFTA)
- Online Boutique
- Mobile Application
- Food Delivery
- Real Estate
- Business Continuity Plan
- Buy Side Due Diligence Services
- ICO whitepaper
- ICO consulting services
- Confidential Information Memorandum
- Private Placement Memorandum
- Feasibility study
- Fractional CFO
- Business Valuation
- How it works
- Business Plan Templates
Operations and Management Business Plan (+Sample in PDF)
Published Aug.03, 2023
Updated Sep.14, 2024
By: Alex Silensky
Average rating 5 / 5. Vote count: 2
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.

Table of Content
1. What Is a Management and Operations Plan?
RephraseA management and operations plan is a crucial document that outlines the direction and management of an organization or enterprise. Typically created with a specific objective in mind, such as achieving company growth, expanding operations, or launching new products, this plan details the organization’s goals and objectives. It provides a roadmap for achieving these goals, serves as a reference for monitoring progress, and allows for necessary adjustments along the way.
The plan provides a comprehensive outline of the roles and responsibilities of every manager and staff member within the organization. This crucial information ensures effective coordination among the management team and helps facilitate goal attainment. Additionally, a well-developed management and operations plan plays a significant role in attracting and retaining investors and customers.
2. Management and operations business plan Sample
The following management and operations business plan will be based on the successful startup of a new facility management business. Professional Business Planning service is focused on creating a sustainable facility management business that prioritizes delivering a unique customer experience through comprehensive services and cost-effective solutions.
Facility Management
The main focus will be on providing tailored Facility Management services to our clients. These services may include facilities maintenance, energy management, environmental compliance, landscaping, housekeeping, and security. We also offer after-hours support and maintenance to ensure all client needs are met professionally and in a timely manner.
The strategic and business plan operations management will maintain a comprehensive inventory of facility management supplies, crisis management, and equipment, including tools, cleaning and janitorial supplies, and appliance parts. The business will also keep inventory of safety supplies, including non-slip mats, fire extinguishers, and first-aid kits.
Objectives and Goals
The primary goal of the management and operations of a business plan is to establish a reputation as a reliable and trusted provider of facility management services. The components indicated in the operations and management section of the business plan will strive to develop and maintain close relationships with clients to provide the highest quality of service possible. A business plan’s operations and management section will also work to ensure that each client is satisfied with the quality and value of the services they receive.
The best business plans to launch its facility management services no later than six months after beginning operations. Initially, the business plan management operation and organization will focus on acquiring new clients and establishing a quality service process. After this initial stage, the business will aim to grow its services and customer reach by targeting nearby communities and neighboring businesses.
Employees and Organizational Structure
The management and operations in the business plan will employ a full-time staff of three and three part-time employees. The staff will have several key responsibilities, including scheduling services, addressing customer inquiries, managing facilities, and keeping track of inventory. They will also undergo comprehensive training to ensure excellent customer service. The business will also have a dedicated service technician available on-call and an administrative assistant to handle customer inquiries and scheduling.
3. Operations and management business plan examples
When developing a business plan for operations and management, it’s crucial to carefully consider the unique goals and objectives of the business. For instance, if you’re starting a restaurant, you need to give careful thought to aspects such as menu options, operating hours, staffing requirements, and other factors that are vital for ensuring the success of your establishment. The same consideration must be given when starting a salon, home care business, or law firm. Running different types of establishments requires a tailored approach, including specific staffing and policies. Creating a successful operations and management business plan involves taking a holistic view of the business while keeping the customer front and center.
For a restaurant, an operations and management business plan examples should include key elements like the types of foods they will serve, pricing, and a detailed schedule for opening and closing by Professional Business Plan Writers . The Restaurant Business Plan should also include plans for hiring and managing staff and the necessary systems and procedures to ensure the restaurant runs smoothly. A salon will also have to consider how they will attract customers, manage services, and care for client safety and satisfaction. Home care and law firms should include detailed plans for recruiting, selecting, and training staff; organization policies; service offerings; and customer service processes.
Overall, management and operations in a business plan for service should outline all operational processes, personnel management, customer service, and marketing tactics for the business to succeed. From food offerings to staff selection, business owners should clearly outline their plan of action and adhere to their operations and management business plan for success.
4. Unlock the Path to Growth and Profit with OGS Capital: The ‘Go-To’ Management Plan Experts
At OGS Capital, we are experts in operations and management business plan consulting. With over 15 years of experience, our team of skilled business and operations strategists is dedicated to helping businesses like yours achieve growth and profitability. We have a deep understanding of the intricacies involved in developing effective operations and management business plans and specialize in creating personalized strategies that address each client’s unique needs.
We provide Professional Business Planning Services, starting with our thorough business assessment services. Our consultants offer personalized guidance based on their extensive industry expertise.
At our company, we prioritize strategic customer targeting in our operations and management business plan development services. Our expertise lies in creating accurate customer segmentation models and impactful market positioning plans. These plans enable you to effectively identify the most suitable customers for your products and services, maximizing your chances of capturing your target market.
With OGS Capital by your side every step of the way, you can be confident that your plan will be completed to the highest quality and efficacy standards. Contact us today to unlock your path to success.

Q.How do you write management and operations in a business plan?
In the management and operations section of a business plan, it is crucial to provide details about the various tasks required to run your business and the roles and responsibilities of each team member. This section should address important questions such as who makes decisions, who handles daily operations, and how the staff hierarchy is structured. Additionally, you should include information on how the business acquires resources and manages finances.
Q.What is an example of an operation management plan?
An example of an operational management plan is a comprehensive blueprint that outlines strategies and steps to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of producing and delivering goods and services. This plan includes specific details about procedures for improving processes, selecting equipment, allocating labor resources, managing inventory, and ensuring quality control. It also encompasses provisions for monitoring, evaluating, and making adjustments to operational changes. Furthermore, the plan identifies potential risks and provides strategies to mitigate them effectively.
Download Operations and Management Business Plan in PDF
OGSCapital’s team has assisted thousands of entrepreneurs with top-rated document, consultancy and analysis. They’ve helped thousands of SME owners secure more than $1.5 billion in funding, and they can do the same for you.

Any questions? Get in Touch!
We have been mentioned in the press:
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Search the site:

COMMENTS
Jul 30, 2023 · An operations plan is a plan to establish, expand or improve the day-to-day processes and practices of a business. Operations includes everything that a business does on a repeated basis to deliver products and services. It is common for operations to be heavily optimized, expanded and improved in order to build competitive advantages, cut ...
Aug 21, 2024 · In your business plan, the operations plan section describes the physical necessities of your business's operation, such as your physical location, facilities, and equipment. Depending on what kind of business you'll be operating, it may also include information about inventory requirements, suppliers, and a description of the manufacturing ...
Jun 26, 2024 · It provides details on resources, wise investments, and effective risk management, ensuring that decisions improve overall business operations. Operations plan essentials. Now that you have understood the importance of the operations plan, let’s go through the essentials of an operations plan: Strategic plan
Feb 24, 2023 · Related Operations Management Content. Operational Strategy: A Quick Guide; Operations Management: Key Functions, Roles and Skills; Operational Efficiency: A Quick Guide; Using Operational Excellence to Be More Productive; Operational planning isn’t done in a silo, and it doesn’t work without the full weight of the team backing it up.
Feb 1, 1997 · The operations plan will highlight the logistics of the organization such as the various responsibilities of the management team, the tasks assigned to each division within the company, and ...
Sep 14, 2024 · The management and operations in the business plan will employ a full-time staff of three and three part-time employees. The staff will have several key responsibilities, including scheduling services, addressing customer inquiries, managing facilities, and keeping track of inventory.